Product Description
Casting Large Ball Mill or Rotary Kiln Spur Gear
Advantages:
– Products with Customers’ Designs
– Strong Machining & Heat Treatment Abilities
– Strict Quality Control
– Prompt Delivery
-Experience in Cooperation with Fortune 5
| Application: | Machinery, Ball Mill and Rotary Kiln |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cast Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
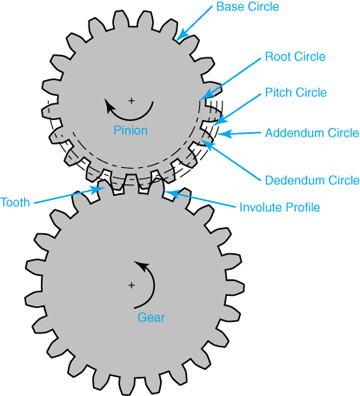
Can spur gears be used in automotive applications?
Yes, spur gears can be used in automotive applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are one of the simplest and most commonly used types of gears. They consist of cylindrical teeth that are parallel to the gear axis and mesh with each other to transmit power and motion. While other gear types like helical gears or bevel gears are often preferred in certain automotive applications, spur gears still find their place in various automotive systems and components.
1. Transmissions:
Spur gears are commonly found in manual transmissions, especially in lower gears. They are used to achieve a direct and efficient power transfer between the engine and the wheels. Spur gears in transmissions are designed to handle high torque loads and provide reliable performance.
2. Differential:
In automotive differentials, which distribute power between the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, spur gears are often employed. They are used in the differential gear train to transfer torque from the driveshaft to the wheels. The simplicity and robustness of spur gears make them suitable for this application.
3. Starter Motors:
Spur gears are commonly used in starter motors to crank the engine when starting a vehicle. They provide high torque and efficient power transmission to rotate the engine’s crankshaft and initiate the combustion process. Starter motor spur gears are designed to handle the initial load and engage smoothly with the engine’s flywheel.
4. Timing Systems:
In automotive timing systems, where precise synchronization of engine components is crucial, spur gears can be used. They are employed in timing belts or chains to drive the camshafts, ensuring proper valve timing and engine performance. Spur gears in timing systems contribute to accurate and reliable engine operation.
5. Accessories and Auxiliary Components:
Spur gears are also utilized in various automotive accessories and auxiliary components. They can be found in power window mechanisms, windshield wipers, power steering systems, and other mechanisms that require controlled and synchronized motion. Spur gears provide cost-effective and efficient power transmission for these applications.
It’s important to note that while spur gears have their advantages, they also have certain limitations. They can generate more noise and vibration compared to gears with helical or bevel tooth profiles. Additionally, spur gears are not as suitable for high-speed or high-torque applications as other gear types.
Overall, spur gears have a significant presence in automotive applications, particularly in manual transmissions, differentials, starter motors, timing systems, and various auxiliary components. Their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a viable choice for specific automotive gear applications.

Can you provide examples of machinery that use spur gears?
Spur gears are widely used in various machinery and mechanical systems due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. Here are some examples of machinery and equipment that commonly utilize spur gears:
- Automotive Industry: Spur gears are found in various automotive applications, including manual transmissions, differential gears, and starter motors. They are used to transmit power and torque efficiently in these systems.
- Mechanical Clocks and Watches: Traditional mechanical clocks and watches often utilize spur gears to transfer rotational motion from the mainspring to the hour, minute, and second hands. These gears play a crucial role in accurate timekeeping.
- Printing Presses: Spur gears are employed in printing presses to synchronize the movement of different components, such as rollers and paper feed mechanisms. They ensure precise and coordinated operation during the printing process.
- Industrial Machinery: Many types of industrial machinery rely on spur gears, including conveyors, packaging equipment, textile machinery, and machine tools. Spur gears help transmit power and control the movement of various components in these machines.
- Power Plants: Spur gears can be found in power generation facilities, such as steam turbines and gas turbines. They help transfer rotational motion from the turbine shaft to the generator shaft, enabling the production of electrical power.
- Agricultural Equipment: Agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters, often utilize spur gears in their drive systems. These gears help transmit power from the engine to the wheels or other operational components.
- Robotics and Automation Systems: Spur gears are commonly used in robotics and automation systems to transmit power and control the movement of robotic arms, conveyor systems, and other mechanical components.
- Power Tools: Many power tools, including drills, saws, and grinders, incorporate spur gears in their gearboxes. These gears help increase torque and provide the necessary speed reduction for efficient tool operation.
These examples represent just a few of the many applications where spur gears are utilized. Spur gears’ simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ability to handle high load capacities make them suitable for a wide range of machinery and mechanical systems in various industries.
It’s important to note that different gear types, such as helical gears, bevel gears, or planetary gears, may also be used in conjunction with spur gears or in different applications depending on specific requirements and design considerations.
Are there different sizes and configurations of spur gears available?
Yes, there are various sizes and configurations of spur gears available to suit different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different options when it comes to sizes and configurations of spur gears:
Sizes: Spur gears come in a wide range of sizes to accommodate different torque and speed requirements. The size of a spur gear is typically specified by its pitch diameter, which is the diameter of the pitch circle. The pitch diameter determines the gear’s overall size and the spacing between the teeth. Spur gears can range from small gears used in precision instruments to large gears used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Module: Module is a parameter used to specify the size and spacing of the teeth on a spur gear. It represents the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth. Different module sizes are available to accommodate various gear sizes and applications. Smaller module sizes are used for finer tooth profiles and higher precision, while larger module sizes are used for heavier loads and higher torque applications.
Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on a spur gear can vary depending on the specific application. Gears with a higher number of teeth provide smoother operation and distribute the load more evenly, whereas gears with fewer teeth are typically used for higher speeds and compact designs.
Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is an important parameter that determines the shape and engagement of the teeth. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees. The selection of the pressure angle depends on factors such as load capacity, efficiency, and specific design requirements.
Profile Shift: Profile shift is a design feature that allows modification of the tooth profile to optimize the gear’s performance. It involves shifting the tooth profile along the gear’s axis, which can affect factors such as backlash, contact ratio, and load distribution. Profile shift can be positive (when the tooth profile is shifted towards the center of the gear) or negative (when the tooth profile is shifted away from the center).
Hub Configuration: The hub refers to the central part of the gear where it is mounted onto a shaft. Spur gears can have different hub configurations depending on the specific application. Some gears have a simple cylindrical hub, while others may have keyways, set screws, or other features to ensure secure and precise mounting.
Material and Coatings: Spur gears are available in various materials to suit different operating conditions and requirements. Common materials include steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic. Additionally, gears can be coated or treated with surface treatments such as heat treatment or coatings to enhance their wear resistance, durability, and performance.
Mounting Orientation: Spur gears can be mounted in different orientations depending on the application and space constraints. They can be mounted parallel to each other on parallel shafts, or they can be mounted at right angles using additional components such as bevel gears or shafts with appropriate bearings.
In summary, there is a wide range of sizes and configurations available for spur gears, including different pitch diameters, module sizes, number of teeth, pressure angles, profile shifts, hub configurations, materials, coatings, and mounting orientations. The selection of the appropriate size and configuration depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, load capacity, space constraints, and specific application needs.


editor by CX 2023-11-14