Product Description
| Product type | Sintered metal parts / Planetary Sun Drive Spur Gea |
| Material | Stainless steel,Steel(Iron,)Brass,Copper (According to product design requirements) |
| Tolerance | ±0.01mm |
| Surface Treatment | As your requirement |
| Application | Tool industry,Automotive, instrument, electrical equipment, household appliances, furniture, mechanical equipment,daily living equipment, electronic sports equipment, light industry products, sanitation machinery, etc. |
| Shape | Any other material and dimension depends on customers’ demand. |
| QC system | 100% inspection before shipment |
| Returned Goods Managing | With quality problem or deviation from drawings |
| Warranty | Replacement at all our cost for rejected products |
| Payment terms | T/T at sight, Paypal, Western Union,etc. |
| Lead time | 7-15 working days as usual,It will based on the detailed order quantity. |
| Why Choose Us |
1. We have professional powder metallurgy production equipment and team;
2. We can accompany customers to develop products;
3. Just send an idea that you want to try, you don’t even need to know what powder metallurgy;
4. Our sales will reply you within 24 hours to confirm further details and give the estimated quote time;
5. Our team will evaluate your inquiry and provide our offer within next 1~3 working days.
| Order Process |
1. You send us drawing or sample.
2. We carry through project assessment.
3. We give you our design for your confirmation.
4. We make the sample and send it to you after you confirmed our design.
5. You confirm the sample then place an order and pay us deposit.
6. We start producing.
7. When the goods is done, you pay us the balance after you confirmed pictures or tracking numbers.
8. Trade is done, thank you!!
Additional Capabilities CAD Design Services CAM Programming Services Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) Reverse Engineering
| Product Show |
| Some Parts We Manufacture |
Self-Lubricated Bushing
Structural Parts
Gears
| About Us |
| Design Tips: Powder Metallurgy Gears |
1. Radius > 0.25 mm is required to manufacture the die;
2. Helical teeth should feature a helical angle < 30º in order to limit side pressure on the punches;
3. Introduction of a draft angle > 5º in the upper diameter reduce the tooling cost;
4. The distance between tooth root and central hub diameter must be: > 3 mm (Robust Tooling).
If you want to know more about the product, please send us a message.
| The Powder Metallurgy Manufacturing Process |
| FAQ |
| Q: How can I get the quotation? |
| A: Please send us information for quote: drawing, material, weight, quantity and request,w can accept PDF, ISGS, DWG, STEP file format. If you don’t have drawing, please send the sample to us,we can quote based on your sample too. |
| Q: What’s your MOQ? |
| A: In general 1000pcs,but can accept low quantity in some special conditions. |
| Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ? |
| A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight. |
| Q: What about the leading time for mass production? |
| A: Honestly, it depends on the order quantity. Normally, 15 days to 20 days after your deposit if no tooling needed. |
| Q: What if the parts are not good? |
| A: We can guarantee good quality,but if happened,please contact us immediately, take some pictures, we will check on the problem,and solve it asap. |
| Q: What is your terms of payment ? |
| A: Payment=1000USD, 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment |
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
To be negotiated |
|---|
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing spur gears?
Designing and manufacturing spur gears involve several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing spur gears:
- Gear Tooth Design: Designing the gear tooth profile is a critical aspect of gear design. Achieving the desired tooth shape, pressure angle, and tooth thickness distribution while considering factors such as load capacity, durability, and noise generation can be challenging. Iterative design processes, computer-aided design (CAD) software, and gear design expertise are often employed to overcome these challenges.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material for gear manufacturing is crucial. Gears need to withstand high loads, transmit power efficiently, and exhibit excellent wear resistance. Selecting materials with suitable hardness, strength, and fatigue resistance can be challenging, especially when considering factors such as cost, availability, and compatibility with other components in the gear system.
- Manufacturing Processes: The manufacturing processes for producing spur gears, such as hobbing, shaping, or broaching, can present challenges. Achieving precise gear tooth profiles, accurate dimensions, and proper surface finish requires advanced machining techniques, specialized equipment, and skilled operators. Maintaining tight tolerances and ensuring consistent quality during mass production can also be demanding.
- Tooth Surface Finish: The surface finish of gear teeth plays a crucial role in gear performance. Achieving a smooth and precise tooth surface finish is challenging due to factors such as tool wear, heat generation during manufacturing, and the complexity of the gear tooth profile. Surface finishing processes, such as grinding or honing, may be required to achieve the desired surface quality.
- Noise and Vibration: Gears can generate noise and vibration during operation, which can affect the overall performance and user experience. Designing gears to minimize noise and vibration requires careful consideration of factors such as tooth profile optimization, load distribution, gear meshing characteristics, and proper lubrication. Conducting noise and vibration analysis and implementing appropriate design modifications may be necessary to address these challenges.
- Backlash Control: Controlling backlash, the slight gap between mating gear teeth, can be challenging. Backlash affects gear accuracy, smoothness of operation, and the ability to transmit torque efficiently. Balancing the need for adequate backlash to accommodate thermal expansion and minimize gear engagement issues while ensuring precise control of backlash can be a complex task in gear design and manufacturing.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes, such as carburizing or quenching, are often employed to enhance the hardness and strength of gear teeth. Proper heat treatment is crucial to achieve the desired material properties and gear performance. However, challenges such as distortion, residual stresses, and material property variations can arise during heat treatment, requiring careful process control, post-heat treatment machining, or additional treatments to mitigate these challenges.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality and reliability of spur gears is a challenge in manufacturing. Implementing effective quality control measures, such as dimensional inspections, hardness testing, and gear tooth profile analysis, is essential. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques and quality assurance systems help monitor manufacturing processes, identify potential issues, and maintain consistent gear quality.
- Cost and Time Constraints: Designing and manufacturing spur gears that meet performance requirements within cost and time constraints can be challenging. Balancing factors such as material costs, tooling expenses, production lead times, and market competitiveness requires careful consideration and optimization. Efficient production planning, cost analysis, and value engineering techniques are often employed to address these challenges.
By recognizing these challenges and employing appropriate design methodologies, manufacturing techniques, and quality control measures, it is possible to overcome the potential challenges associated with designing and manufacturing spur gears.
It’s important to note that the specific challenges may vary depending on the gear application, size, complexity, and operating conditions. Collaboration with gear design experts, manufacturing engineers, and industry specialists can provide valuable insights and guidance in addressing the challenges specific to your spur gear design and manufacturing processes.
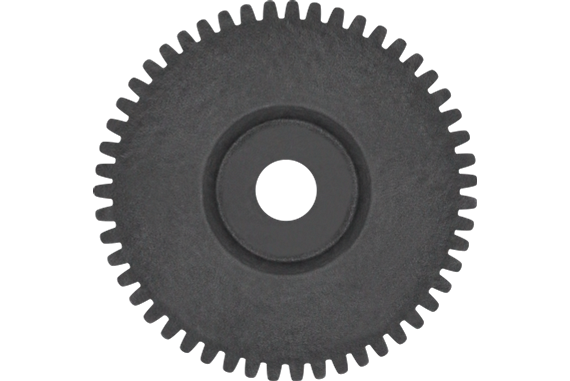
What is the purpose of using spur gears in machinery?
In machinery, spur gears serve several important purposes due to their unique characteristics and capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purpose of using spur gears in machinery:
- Power Transmission: Spur gears are primarily used for power transmission in machinery. They transfer rotational motion and torque from one shaft to another, allowing machinery to perform various tasks. By meshing the teeth of two or more spur gears together, power can be transmitted efficiently and reliably throughout the machinery.
- Speed Reduction or Increase: Spur gears enable speed reduction or increase in machinery. By combining gears with different numbers of teeth, the rotational speed can be adjusted to match the desired output speed. For example, using a larger gear driving a smaller gear can increase the speed output while reducing the torque, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the speed while increasing the torque.
- Torque Amplification: Spur gears can amplify torque in machinery. By using gears with different numbers of teeth, the torque can be adjusted to match the required output. For example, using a smaller gear driving a larger gear can increase the torque output while reducing the speed, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the torque while increasing the speed.
- Directional Control: Spur gears provide directional control in machinery. By meshing gears with opposite orientations, the rotational direction of the driven shaft can be reversed or changed. This directional control is crucial for machinery that requires bi-directional motion or needs to change the direction of operation.
- Mechanical Advantage: Spur gears offer a mechanical advantage in machinery. By utilizing gear ratios, spur gears can multiply or divide the force exerted on the input shaft. This mechanical advantage allows machinery to generate higher forces or achieve precise movements with reduced effort.
- Precision Positioning: Spur gears facilitate precise positioning in machinery. The accurate tooth engagement of spur gears ensures precise control over rotational motion, making them suitable for applications that require precise positioning or synchronization of components. Machinery such as CNC machines, robotics, and automation systems often rely on spur gears for accurate movement and positioning.
- Compact Design: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for machinery with space constraints. They can be arranged in-line, parallel, or at right angles, allowing for efficient power transmission in tight spaces. Their compactness enables machinery to be designed with smaller footprints and optimized layouts.
- Reliability and Durability: Spur gears are known for their reliability and durability in machinery. The direct tooth engagement and uniform load distribution result in efficient power transmission with reduced wear and stress concentration. When properly lubricated and maintained, spur gears can withstand heavy loads and operate reliably over extended periods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Spur gears are often cost-effective in machinery applications. Their simple design and ease of manufacturing contribute to lower production costs. Additionally, their high efficiency helps reduce energy consumption, resulting in potential long-term cost savings. The availability of spur gears in various sizes and materials further enhances their cost-effectiveness.
By utilizing spur gears in machinery, engineers and designers can achieve efficient power transmission, speed and torque control, directional versatility, mechanical advantage, precise positioning, compact design, reliability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. These advantages make spur gears a popular choice in a wide range of machinery applications across industries.
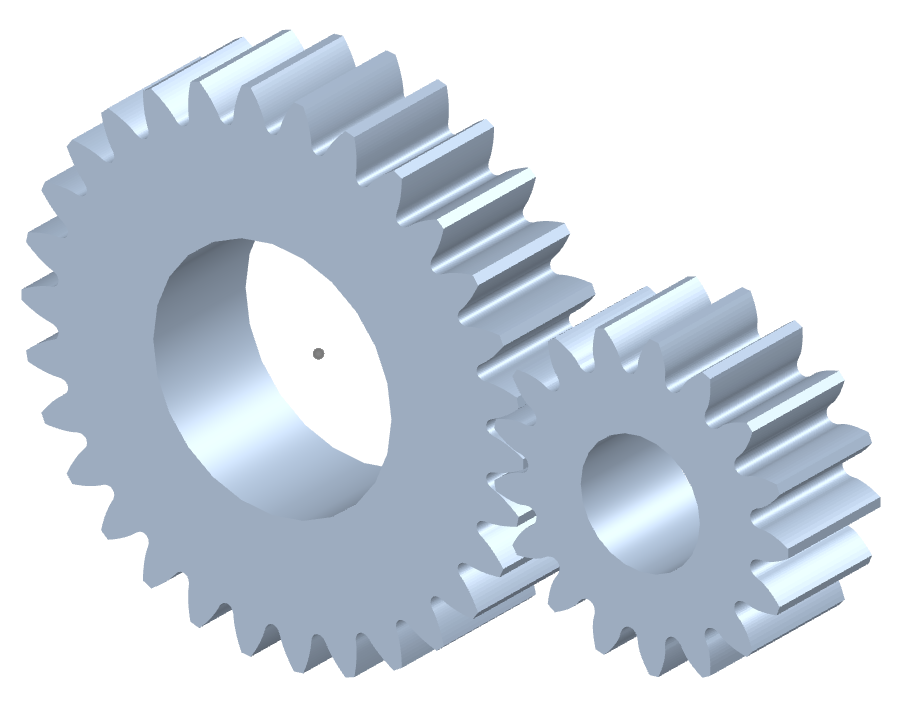
Can you explain the concept of straight-cut teeth in spur gears?
The concept of straight-cut teeth is fundamental to understanding the design and operation of spur gears. Straight-cut teeth, also known as straight teeth or parallel teeth, refer to the shape and arrangement of the teeth on a spur gear. Here’s a detailed explanation of the concept of straight-cut teeth in spur gears:
Spur gears have teeth that are cut straight and parallel to the gear axis. Each tooth has a uniform width and thickness, and the tooth profile is a straight line. The teeth are evenly spaced around the circumference of the gear, allowing them to mesh with other spur gears.
The key characteristics and concepts related to straight-cut teeth in spur gears include:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of a spur gear with straight-cut teeth is a straight line that extends radially from the gear’s pitch circle. The profile is perpendicular to the gear axis and remains constant throughout the tooth’s height.
- Pitch Circle: The pitch circle is an imaginary circle that represents the theoretical point of contact between two meshing gears. For a spur gear, the pitch circle is located midway between the gear’s base circle (the bottom of the tooth profile) and the gear’s addendum circle (the top of the tooth profile).
- Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is the angle between the line tangent to the tooth profile at the pitch point and a line perpendicular to the gear axis. It determines the force distribution between the meshing teeth and affects the gear’s load-bearing capacity and efficiency. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees.
- Meshing: Straight-cut teeth in spur gears mesh directly with each other. The teeth engage and disengage along a line contact, creating a point or line contact between the contacting surfaces. This direct meshing arrangement allows for efficient power transmission and motion transfer.
- Advantages and Limitations: Straight-cut teeth offer several advantages in spur gears. They are relatively simple to manufacture, resulting in cost-effective production. Moreover, they provide efficient power transmission and are suitable for moderate to high-speed applications. However, straight-cut teeth can generate more noise and vibration compared to certain other tooth profiles, and they may experience higher stress concentrations under heavy loads.
In summary, straight-cut teeth in spur gears refer to the straight and parallel arrangement of the gear’s teeth. The teeth have a uniform profile with a constant width and thickness. Understanding the concept of straight-cut teeth is essential for designing and analyzing spur gears, considering factors such as tooth profile, pitch circle, pressure angle, meshing characteristics, and the trade-offs between simplicity, efficiency, and noise considerations.


editor by CX 2023-09-21