Product Description
Company Information:
HangZhou Engineering Plastics Industries Co., Ltd, is the professional manufacturer of engineering plastic products.We are a free technical supplier,which have advanced automated production equipment,and very familiar with property of all kinds of plastics material.
White MC Nylon gear with best self-lubrication
Mc nylon, means monomer casting nylon, is a kind of engineering plastics used in comprehensive industries, has been applied almost every industrial field.
The caprolactam monomer is first melted, and added catalyst, then poured it inside moulds at atmosphere pressure so as to shape in different castings, such as:Rod, plate, tube.The molecule weight of mc nylon can reach 70, 000-100, 000/mol, 3 times than pa6/pa66.Its mechanical properties are much higher than other nylon materials, such as:Pa6/pa66.Mc nylon plays a more and more important role in the material list recommended by our country.
Main Characteristics MC Nylon Gear:
1.Good wear-resistance
2.Good corrosion-resistance
3.High self-lubrication
4.High vibration-absorption
5.High noise-absorption
The property of MC Nylon Gear :
| Property | Item No. | Unit | MC Nylon (Natural) | Oil Nylon+Carbon (Black) | Oil Nylon (Green) | MC90 (Blue) | MCNylon+MSO2(Light Black) | |
| Mechanical Properties | 1 | Density | g/cm3 | 1.15 | 1.15 | 1.135 | 1.15 | 1.16 |
| 2 | Water absorption (23ºCin air) | % | 1.8-2.0 | 1.8-2.0 | 2 | 2.3 | 2.4 | |
| 3 | Tensile strength | MPa | 89 | 75.3 | 70 | 81 | 78 | |
| 4 | Tensile strain at break | % | 29 | 22.7 | 25 | 35 | 25 | |
| 5 | Compressive stress (at 2%nominal strain) | MPa | 51 | 51 | 43 | 47 | 49 | |
| 6 | Charpy impact strength (unnotched) | KJ/m 2 | No brak | No break | ≥50 | No BK | No break | |
| 7 | Charpy impact strength (notched) | KJ/m 2 | ≥5.7 | ≥6.4 | 4 | 3.5 | 3.5 | |
| 8 | Tensile modulus of elasticity | MPa | 3190 | 3130 | 3000 | 3200 | 3300 | |
| 9 | Ball indentation hardness | N/mm 2 | 164 | 150 | 145 | 160 | 160 | |
| 10 | Rockwell hardness | – | M88 | M87 | M82 | M85 | M84 | |
Application of MC Nylon Gear:
1.Chemical Engineering
2.Electric/Electronic industry
3.Auto industry
4.Packing machine
5.Engineering machine
6.Pharmaceutical/equipment industry
Our Service:
1. Rich industry experience since 1988.
2. Wide arrange product line, including plastics sheet/rod/parts/accessories: MC NYLON, OIL NYLON, POM, UHMW-PE, PU, PETP, PC, PTFE, PVDF, PPS, PEEK, PAI, PI, PBI ect.
3. Manufacture, design and processing service as per your demand.
Production Flow:
Product technology:
CNC machine,Extrusion,Injection,ect.
Processing Equipment :
CNC machining center,CNC lathes,Milling,Injection Molding Machine,Extruder,Moulding press
Packaging &Shipping:
Packing in plastics bags,wooden case,pallet,container,ect.
Certificate:
Certification:ISO,SGS,FDA,RoHS,Test report,ect.
FAQ:
1.A: What’s the size of plastics sheet?
B:Nylon sheet:Thickness*Width*Length:20-100*1000*2000mm
UHMW-PE sheet:Thickness*Width*Length:20-100*1000*2000mm; 20-100*1250*3130mm; 20-100*1250*4250mm
POM sheet:Width*Length:1000*2000mm
2. A:Can we purchase a small part of plastics sheet?
B: Yes,you can, if we have the size you require in stock.
3. A:What color of plastics sheet?
B: Nylon sheet: Natural,black,blue,or according to client’s requiremnet.
UHMW-PE sheet: White,black,green ,bule,yellow,or according to client’s requirement.
White,black
4. A:Can you manufacture the plastics products as per drawing?
B: Yes,we can.
5.A: What the precision of plastic products according to drawing?
B: Different machine with different precision,it usually around 0.05-0.1mm
6.A: What the technologies in producing plastics parts?
B: Different products with different technologies,such as CNC machine,Extrusion,Injection
7: A:What kinds of processing machine do you have?
B: CNC machining center,CNC lathes,Milling,Injection Molding Machine,Extruder,Moulding press /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | PA |
|---|---|
| Size: | According to Drawing or Sample |
| Color: | Natural, White, Black, Green, Blue |
| Tooling: | CNC Lathe |
| Density: | 1.2 |
| Application: | Food and Beverage Light Industry, Electronic Indust |
| Samples: |
US$ 2/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
Can spur gears be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment?
Yes, spur gears can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are versatile and commonly used in a wide range of applications, including heavy-duty machinery and equipment. They are known for their simplicity, efficiency, and ability to transmit high loads and torque. Spur gears have straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis, allowing for effective power transmission between parallel shafts.
Advantages of Spur Gears in Heavy-Duty Applications:
Spur gears offer several advantages that make them suitable for heavy-duty machinery and equipment:
- High Load Capacity: Spur gears are capable of handling high loads due to their robust tooth design and larger contact area compared to other gear types. They distribute the load evenly across the gear teeth, minimizing stress concentration and ensuring reliable operation in heavy-duty applications.
- Efficient Power Transmission: Spur gears have high gear meshing efficiency, typically above 95%. This means that a large percentage of the input power is effectively transmitted to the output, making them suitable for heavy-duty machinery where power transfer is critical.
- Wide Range of Sizes and Ratios: Spur gears are available in a wide range of sizes, tooth counts, and gear ratios. This versatility allows for customization and adaptation to the specific requirements of heavy-duty machinery and equipment.
- Cost-Effective: Spur gears are relatively simple in design and easier to manufacture compared to some other gear types. This simplicity often translates into cost-effectiveness, making them an attractive choice for heavy-duty applications where cost considerations are important.
- Easy Maintenance: Spur gears are generally easier to maintain compared to gears with complex tooth profiles or specialized designs. Routine maintenance tasks such as lubrication, inspection, and replacement of worn gears can be carried out more straightforwardly, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
Considerations for Heavy-Duty Applications:
While spur gears can be used in heavy-duty machinery and equipment, certain considerations should be taken into account:
- Load Distribution: Proper load distribution is critical to ensure the longevity and reliability of spur gears in heavy-duty applications. It is important to design the gear system in a way that distributes the loads evenly across the gear teeth, minimizing the risk of tooth breakage or premature wear.
- Material Selection: The selection of gear materials is crucial in heavy-duty applications. The gear material should have the necessary strength, hardness, and fatigue resistance to withstand the anticipated loads and operating conditions. Common materials used for heavy-duty spur gears include alloy steels, case-hardened steels, and specialized gear materials such as carburized or nitrided steels.
- Lubrication and Cooling: Adequate lubrication is essential to minimize friction, wear, and heat generation in heavy-duty spur gears. Proper lubrication techniques and the use of high-quality lubricants can significantly extend the gear’s service life. In some cases, additional cooling measures such as circulating oil systems or forced-air cooling may be necessary to manage heat buildup in heavy-duty applications.
- Mechanical Considerations: The overall mechanical design of the heavy-duty machinery should account for gear alignment, shaft deflection, and other factors that can affect gear performance. Robust support structures, accurate alignment, and consideration of potential misalignments due to operational conditions should be taken into account during the design phase.
By addressing these considerations and implementing proper design, material selection, lubrication, and maintenance practices, spur gears can effectively withstand the demands of heavy-duty machinery and equipment.
It’s important to note that the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and load characteristics may vary. Consulting with gear manufacturers, engineers, or industry experts can provide further guidance on the suitability and design considerations when using spur gears in heavy-duty applications.
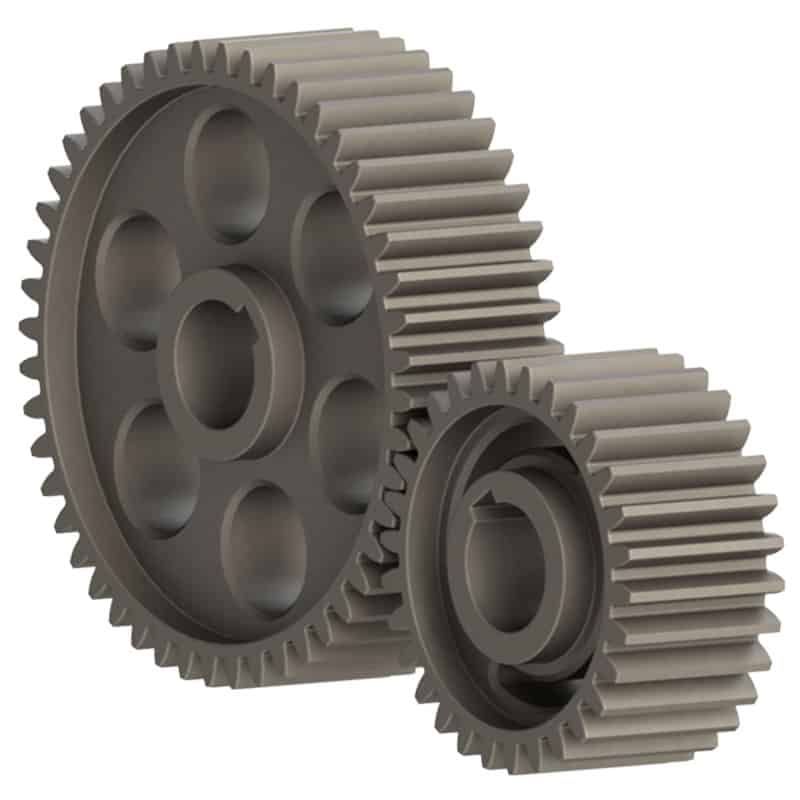

How do you install a spur gear system?
Installing a spur gear system involves several steps to ensure proper alignment, engagement, and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to install a spur gear system:
- Preparation: Before installation, gather all the necessary components, including the spur gears, shafts, bearings, and any additional mounting hardware. Ensure that the gear system components are clean and free from debris or damage.
- Shaft Alignment: Proper shaft alignment is crucial for the smooth operation of a spur gear system. Ensure that the shafts on which the gears will be mounted are aligned accurately and parallel to each other. This can be achieved using alignment tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems. Adjust the shaft positions as needed to achieve the desired alignment.
- Positioning the Gears: Place the spur gears on the respective shafts in the desired configuration. Ensure that the gears are positioned securely and centered on the shafts. For shafts with keyways, align the gears with the key and ensure a proper fit. Use any necessary mounting hardware, such as set screws or retaining rings, to secure the gears in place.
- Checking Gear Engagement: Verify that the teeth of the gears mesh properly with each other. The gear teeth should align accurately and smoothly without any excessive gaps or interference. Rotate the gears by hand to ensure smooth and consistent meshing throughout their rotation. If any misalignment or interference is observed, adjust the gear positions or shaft alignment accordingly.
- Bearing Installation: If the spur gear system requires bearings to support the shafts, install the bearings onto the shafts. Ensure that the bearings are the correct size and type for the application. Press or slide the bearings onto the shafts until they are seated securely against any shoulder or bearing housing. Use appropriate methods and tools to prevent damage to the bearings during installation.
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable lubricant to the gear teeth and bearings to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction. Refer to the gear manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate lubrication type and amount. Proper lubrication helps minimize wear, noise, and heat generation in the gear system.
- Final Inspection: Once the gears, shafts, and bearings are installed, perform a final inspection of the entire spur gear system. Check for any unusual noises, misalignment, or binding during manual rotation. Verify that the gears are securely mounted, shafts are properly aligned, and all fasteners are tightened to the specified torque values.
It’s important to follow the specific installation instructions provided by the gear manufacturer to ensure proper installation and operation. Additionally, consult any applicable industry standards and guidelines for gear system installation.
By carefully following these installation steps, you can ensure a well-aligned and properly functioning spur gear system in your machinery or equipment.

Are there different sizes and configurations of spur gears available?
Yes, there are various sizes and configurations of spur gears available to suit different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different options when it comes to sizes and configurations of spur gears:
Sizes: Spur gears come in a wide range of sizes to accommodate different torque and speed requirements. The size of a spur gear is typically specified by its pitch diameter, which is the diameter of the pitch circle. The pitch diameter determines the gear’s overall size and the spacing between the teeth. Spur gears can range from small gears used in precision instruments to large gears used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Module: Module is a parameter used to specify the size and spacing of the teeth on a spur gear. It represents the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth. Different module sizes are available to accommodate various gear sizes and applications. Smaller module sizes are used for finer tooth profiles and higher precision, while larger module sizes are used for heavier loads and higher torque applications.
Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on a spur gear can vary depending on the specific application. Gears with a higher number of teeth provide smoother operation and distribute the load more evenly, whereas gears with fewer teeth are typically used for higher speeds and compact designs.
Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is an important parameter that determines the shape and engagement of the teeth. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees. The selection of the pressure angle depends on factors such as load capacity, efficiency, and specific design requirements.
Profile Shift: Profile shift is a design feature that allows modification of the tooth profile to optimize the gear’s performance. It involves shifting the tooth profile along the gear’s axis, which can affect factors such as backlash, contact ratio, and load distribution. Profile shift can be positive (when the tooth profile is shifted towards the center of the gear) or negative (when the tooth profile is shifted away from the center).
Hub Configuration: The hub refers to the central part of the gear where it is mounted onto a shaft. Spur gears can have different hub configurations depending on the specific application. Some gears have a simple cylindrical hub, while others may have keyways, set screws, or other features to ensure secure and precise mounting.
Material and Coatings: Spur gears are available in various materials to suit different operating conditions and requirements. Common materials include steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic. Additionally, gears can be coated or treated with surface treatments such as heat treatment or coatings to enhance their wear resistance, durability, and performance.
Mounting Orientation: Spur gears can be mounted in different orientations depending on the application and space constraints. They can be mounted parallel to each other on parallel shafts, or they can be mounted at right angles using additional components such as bevel gears or shafts with appropriate bearings.
In summary, there is a wide range of sizes and configurations available for spur gears, including different pitch diameters, module sizes, number of teeth, pressure angles, profile shifts, hub configurations, materials, coatings, and mounting orientations. The selection of the appropriate size and configuration depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, load capacity, space constraints, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-04-23