Product Description
My advantages:
1. High quality materials, professional production, high-precision equipment. Customized design and processing;
2. Strong and durable, strong strength, large torque and good comprehensive mechanical properties;
3. High rotation efficiency, stable and smooth transmission, long service life, noise reduction and shock absorption;
4. Focus on gear processing for 20 years.
5. Carburizing and quenching of tooth surface, strong wear resistance, reliable operation and high bearing capacity;
6. The tooth surface can be ground, and the precision is higher after grinding.
| Application: | Motor, Motorcycle, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
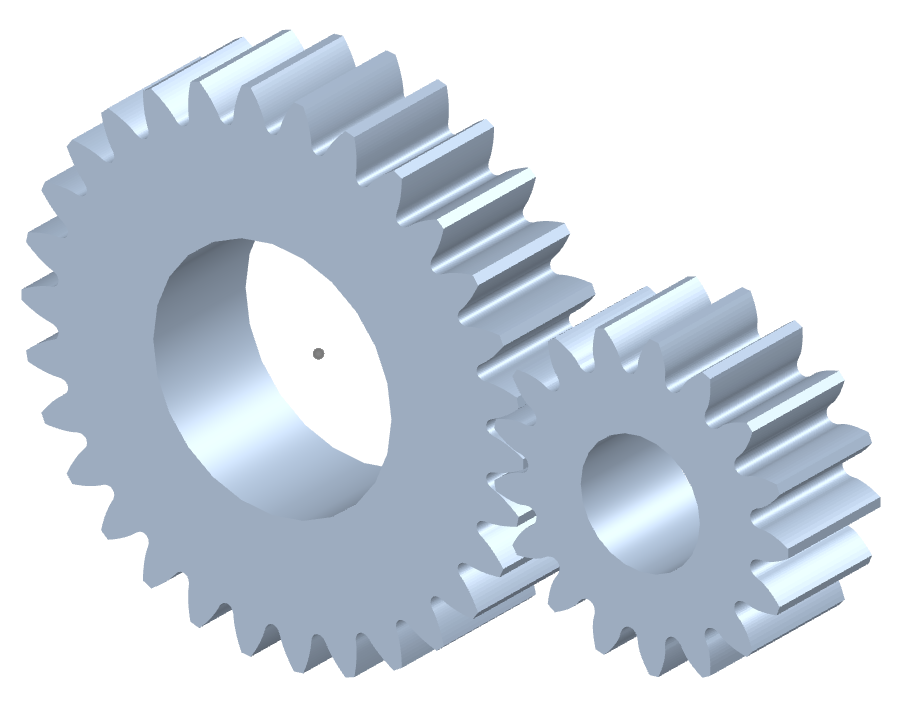
How do you ensure proper alignment when connecting spur gears?
Proper alignment is crucial when connecting spur gears to ensure smooth and efficient gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to ensure proper alignment when connecting spur gears:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the gears, gear shafts, and associated components for any visible misalignment or damage. Look for signs of wear, uneven tooth engagement, or any abnormalities that may affect alignment.
- Shaft Alignment: Align the gear shafts accurately before connecting the gears. Proper shaft alignment ensures that the gears are positioned correctly relative to each other. This can be achieved through various alignment techniques, such as using alignment tools, laser alignment systems, or measuring devices. The goal is to ensure parallel or coaxial alignment between the gear shafts.
- Backlash Adjustment: Adjust the backlash between the gear teeth to achieve proper alignment. Backlash refers to the slight gap between the mating teeth of gears. It is important to maintain an appropriate amount of backlash to allow for smooth gear engagement and minimize the risk of binding or jamming. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations or industry standards for the recommended backlash range and adjust as necessary during gear installation.
- Check Gear Mesh: Verify the gear meshing pattern to ensure proper alignment. The gear teeth should mesh smoothly and evenly without any signs of excessive or uneven contact. If there are indications of improper meshing, such as concentrated contact on a specific area of the tooth, it may imply misalignment or other issues that need to be addressed.
- Shim Adjustment: If misalignment is detected, shimming can be employed to correct it. Shimming involves placing thin metal shims between the gear and the shaft to adjust the positioning and alignment. Shims are available in various thicknesses, allowing for precise alignment adjustments. Careful measurement and selection of the appropriate shim thickness can help achieve the desired alignment.
- Tightening Bolts: When connecting the gears to the shafts, ensure that the bolts or fasteners are tightened evenly and to the recommended torque specifications. Uneven tightening can introduce misalignment or uneven load distribution, leading to gear misalignment and potential issues.
- Post-Installation Verification: After connecting the gears, perform a final verification of the alignment. Rotate the gears manually or through the gear system’s intended operation and observe the gear meshing behavior. Look for any signs of abnormal noise, vibration, or irregular tooth engagement. If any issues are detected, further adjustments or inspections may be necessary.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a proactive maintenance program that includes periodic inspections and alignment verification. Gears can experience wear or misalignment over time due to factors such as load variations, temperature changes, or prolonged operation. Regular maintenance allows for early detection and correction of alignment issues, ensuring optimal gear performance and longevity.
Proper alignment is essential for maximizing the efficiency, durability, and reliability of spur gear systems. By following these alignment practices and considering the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and expert advice, you can ensure proper alignment when connecting spur gears.
It’s important to note that the specific alignment techniques and procedures may vary depending on the gear system’s design, size, application, and other factors. Consulting with gear manufacturers, engineers, or alignment specialists can provide further guidance on the recommended alignment practices for your specific gear system.

Are spur gears suitable for high-torque applications?
Spur gears are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including those involving high-torque requirements. However, their suitability for high-torque applications depends on various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are designed to transmit power and torque between parallel shafts. They have straight teeth that engage fully, providing efficient power transfer. The suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications can be evaluated based on the following considerations:
- Load Distribution: Spur gears distribute the transmitted load over a larger contact area compared to other gear types. This characteristic allows them to handle higher torque loads effectively.
- Size and Diameter: The size and diameter of the spur gears play a crucial role in their ability to handle high torque. Larger gear diameters provide increased torque capacity due to the longer lever arm and larger contact area between the gear teeth.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material for the spur gears is essential for high-torque applications. Strong and durable materials, such as hardened steel or alloy steels, are commonly used to ensure the gears can withstand the high stresses and torque loads without deformation or failure.
- Gear Design: Proper gear design considerations, such as tooth profile, module or pitch, and the number of teeth, can impact the torque-carrying capacity of spur gears. Design parameters should be optimized to ensure sufficient tooth strength and minimize the risk of tooth breakage or excessive wear.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Adequate lubrication is critical for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in high-torque spur gear applications. Regular maintenance, including lubricant replacement and gear inspections, can help identify and address any issues that may affect the gear’s torque-handling capabilities.
- Supporting Components: The overall system design, including the selection of bearings, shafts, and housing, should be considered to ensure proper support and alignment of the spur gears. Well-designed supporting components contribute to the overall torque capacity of the system.
While spur gears can handle high torque, it’s important to note that there are limitations to their torque capacity. Factors such as gear size, material strength, tooth design, and operating conditions can affect the maximum torque the gears can safely transmit without failure.
In some cases, other gear types such as helical gears or bevel gears may be more suitable for specific high-torque applications. These gears offer advantages such as increased load-carrying capacity, improved torque transfer efficiency, and reduced noise and vibration levels.
Ultimately, the suitability of spur gears for high-torque applications should be evaluated based on the specific requirements, operating conditions, and industry standards applicable to the particular application.

What is a spur gear and how does it work?
A spur gear is a type of cylindrical gear with straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. It is one of the most common and simplest types of gears used in various mechanical systems. Spur gears work by meshing together to transmit rotational motion and torque between two parallel shafts. Here’s a detailed explanation of spur gears and how they work:
A spur gear consists of two or more gears with cylindrical shapes and an equal number of teeth. These gears are mounted on parallel shafts, and their teeth mesh together to transfer rotational motion from one gear to another. The gear with power input is called the “drive gear” or “driver,” while the gear receiving the power output is called the “driven gear” or “follower.”
The key characteristics and components of spur gears include:
- Teeth: Spur gears have straight teeth that are cut parallel to the shaft axis. The teeth are evenly spaced around the circumference of the gear. The number of teeth determines the gear ratio and affects the speed and torque transmission between the gears.
- Pitch Diameter: The pitch diameter is the theoretical diameter of the gear at the point where the teeth mesh. It is determined by the number of teeth and the module or diametral pitch of the gear.
- Module or Diametral Pitch: The module is a parameter used in metric gear systems, while the diametral pitch is used in imperial gear systems. They define the tooth size and spacing of the gear. The module is the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth, while the diametral pitch is the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter.
- Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is the angle between the line tangent to the tooth profile at the pitch point and a line perpendicular to the gear axis. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees.
- Meshing: Spur gears mesh by engaging their teeth, creating a point or line contact between the contacting surfaces. The teeth transfer rotational motion and torque from the drive gear to the driven gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the drive gear and the driven gear. It defines the relationship between the input speed and the output speed. The gear ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the driven gear by the number of teeth on the drive gear.
- Operation: As the drive gear rotates, its teeth come into contact with the teeth of the driven gear. The contact between the teeth transfers rotational motion and torque from the drive gear to the driven gear. The meshing teeth maintain a constant speed ratio, allowing for the transmission of power between the shafts. The direction of rotation can be changed by meshing gears with an odd or even number of teeth.
Spur gears offer several advantages, including simplicity, ease of manufacture, efficiency, and reliability. They are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including machinery, automotive systems, appliances, power tools, and more.
In conclusion, spur gears are cylindrical gears with straight teeth that mesh together to transfer rotational motion and torque between parallel shafts. Their simple and efficient design makes them a popular choice for various mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2023-10-26