Product Description
CITICIC is the casting & forging center in central-south China, possessing 50t electric arc furnace, 60t LF ladle refining furnace, and 60t VD/VOD refining furnace, etc. We can pour 350t liquid steel 1 time and yields more than 200,000t of high quality liquid steel and can produce the high quality steel of more than 260 steel grades such as carbon steel, structural alloy steel and the structural steel, refractory steel and stainless steel of special requirement. The maximum weight of casting, gray casting, graphite cast iron and non-ferrous casting is 200t, 30t, 20t and 205t separately.
Features:
Module Range: 10 Module to 70 Module.
Diameter: Min 800mm to16000 mm.
Weight: Max 120 MT single piece.
Three different designs: Fabricated steel – forged ring – rolled plate
Standards / Certificates: • CHINAMFG EN ISO • AWS • ASTM • ASME • DIN
Advantages:
– Products with Customers’ Designs
– Strong Machining & Heat Treatment Abilities
– Strict Quality Control
– Prompt Delivery
– Experience in Cooperation with Fortune 500 Companies
Process:
Forging / Casting
Normalizing & Tempering-Proof Machining
Quenching & Tempering
Finish Machining (Teeth Grinding)
We can offer you in various process conditions solutions for Many End Markets and Applications
–Mining
–Metallurgy
–Power Generation
–Sugar
–Cement Plant
–Port Machinery
–Oil and natural
–Papermaking
–OEM gear case
–General Industrial
Specifications Of Gear:
| No. |
Item |
Description |
|
1 |
Diameter |
≤15m |
|
2 |
Module |
≤45 |
|
3 |
Material |
Cast Alloy Steel, Cast Carbon Steel, Forged Alloy Steel, Forged Carbon Steel |
|
4 |
Structure From |
Integrated, Half to Half, Four Pieces and More Pieces |
|
5 |
Heat Treatment |
Quenching & Tempering, Normalizing & Tempering, Carburizing & Quenching & Tempering |
|
6 |
Tooth Form |
Annular Gear, Outer Gear Ring |
|
7 |
Standard |
ISO, EN, DIN, AISI, ASTM, JIS, IS, GB |
Inspection And Test Outline Of Girth Gear:
| No. |
Item |
Inspection Area |
Acceptance Criteria |
Inspection Stage |
Certificates |
|
1 |
Chemical |
Sample |
Material Requirement |
When Smelting |
Chemical Composition |
|
2 |
Mechanical |
Sample (Test Bar on the Gear Body) |
Technical Requirement |
After Heat Treatment |
Mechanical Properties |
|
3 |
Heat |
Whole Body |
Manufacturing Standard |
During Heat Treatment |
Heat Treatment Report |
|
4 |
Hardness |
Tooth Surface, 3 Points Per 90° |
Technical Requirement |
After Heat Treatment |
Hardness Teat Report |
|
After Semi Finish |
|||||
|
5 |
Dimension |
Whole Body |
Drawing |
After Semi Finish Machining |
Dimension Inspection |
|
Finish Machining |
|||||
|
6 |
Magnetic Power Test (MT) |
Tooth Surface |
Agreed Standard |
After Finish Gear |
MT Report |
|
7 |
UT |
Spokes Parts |
Agreed Standard |
After Rough Machining |
UT Report |
|
After Welded |
|||||
|
After Semi Finish |
|||||
|
8 |
PT |
Defect Area |
No Defect Indicated |
After Digging |
PT Record |
|
9 |
Mark Inspection |
Whole Body |
Manufacturing Standard |
Final Inspection |
Pictures |
|
10 |
Appearance Inspection |
Whole Body |
CIC’s Requirement |
Before Packing (Final Inspection) |
|
|
11 |
Anti-rust |
Whole Body |
Agreed Anti-rust Agent |
Before Packing |
Pictures |
|
12 |
Packing |
Whole Body |
Agreed Packing Form |
During Packing |
Pictures |
Facilities For Manufacturing Gear Ring:
| No |
Item |
Description |
|
1 |
Smelting & Casting Capability |
40t, 50t, 80t Series AC Electric Arc Furnace We can pour 900t refining liquid steel 1 time, and achieve vacuum poured 600t steel ingots. We can produce the high quality steel of more than 260 steel grades as carbon steel, structural alloy steel and the structural steel, refractory steel and stainless steel of special requirement. The maximum weight of casting steel, gray casting, graphite cast iron and non-ferrous casting is 600t, 200t, 150t and 20t separately. |
|
2 |
Forging Capability |
The only 1 in the word, the most technologically advanced and the largest |
|
3 |
Heat Treatment Capability |
9×9×15m, 8×8×12m, 6×6×15m, 15×16×6.5m, 16×20×6m, 7×7×17m Series Heat CHINAMFG and Heat Treatment Furnaces φ2.0×30m, φ3.0×5.0m Series Heat Treatment Furnaces |
|
4 |
Machining Capability |
1. ≥5m CNC Heavy Duty Vertical Lathes 12m CNC Double-column Vertical Lathe
2. ≥5m Vertical Gear Hobbing Machines
3. Imported High-precision Gear Grinding Machines
4. Large Boring & Milling Machines |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | According to Customers′ Requirements |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cast Gear, Forged Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel, Forged Steel |
| Type: | Circular Gear |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
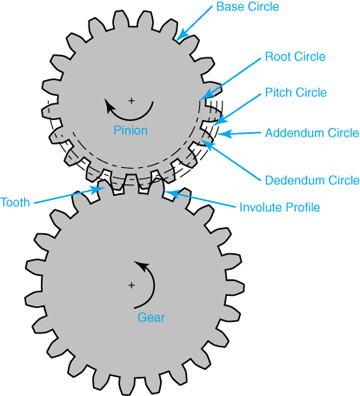
Can spur gears be used in automotive applications?
Yes, spur gears can be used in automotive applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are one of the simplest and most commonly used types of gears. They consist of cylindrical teeth that are parallel to the gear axis and mesh with each other to transmit power and motion. While other gear types like helical gears or bevel gears are often preferred in certain automotive applications, spur gears still find their place in various automotive systems and components.
1. Transmissions:
Spur gears are commonly found in manual transmissions, especially in lower gears. They are used to achieve a direct and efficient power transfer between the engine and the wheels. Spur gears in transmissions are designed to handle high torque loads and provide reliable performance.
2. Differential:
In automotive differentials, which distribute power between the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, spur gears are often employed. They are used in the differential gear train to transfer torque from the driveshaft to the wheels. The simplicity and robustness of spur gears make them suitable for this application.
3. Starter Motors:
Spur gears are commonly used in starter motors to crank the engine when starting a vehicle. They provide high torque and efficient power transmission to rotate the engine’s crankshaft and initiate the combustion process. Starter motor spur gears are designed to handle the initial load and engage smoothly with the engine’s flywheel.
4. Timing Systems:
In automotive timing systems, where precise synchronization of engine components is crucial, spur gears can be used. They are employed in timing belts or chains to drive the camshafts, ensuring proper valve timing and engine performance. Spur gears in timing systems contribute to accurate and reliable engine operation.
5. Accessories and Auxiliary Components:
Spur gears are also utilized in various automotive accessories and auxiliary components. They can be found in power window mechanisms, windshield wipers, power steering systems, and other mechanisms that require controlled and synchronized motion. Spur gears provide cost-effective and efficient power transmission for these applications.
It’s important to note that while spur gears have their advantages, they also have certain limitations. They can generate more noise and vibration compared to gears with helical or bevel tooth profiles. Additionally, spur gears are not as suitable for high-speed or high-torque applications as other gear types.
Overall, spur gears have a significant presence in automotive applications, particularly in manual transmissions, differentials, starter motors, timing systems, and various auxiliary components. Their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a viable choice for specific automotive gear applications.
What is the purpose of using spur gears in machinery?
In machinery, spur gears serve several important purposes due to their unique characteristics and capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purpose of using spur gears in machinery:
- Power Transmission: Spur gears are primarily used for power transmission in machinery. They transfer rotational motion and torque from one shaft to another, allowing machinery to perform various tasks. By meshing the teeth of two or more spur gears together, power can be transmitted efficiently and reliably throughout the machinery.
- Speed Reduction or Increase: Spur gears enable speed reduction or increase in machinery. By combining gears with different numbers of teeth, the rotational speed can be adjusted to match the desired output speed. For example, using a larger gear driving a smaller gear can increase the speed output while reducing the torque, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the speed while increasing the torque.
- Torque Amplification: Spur gears can amplify torque in machinery. By using gears with different numbers of teeth, the torque can be adjusted to match the required output. For example, using a smaller gear driving a larger gear can increase the torque output while reducing the speed, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the torque while increasing the speed.
- Directional Control: Spur gears provide directional control in machinery. By meshing gears with opposite orientations, the rotational direction of the driven shaft can be reversed or changed. This directional control is crucial for machinery that requires bi-directional motion or needs to change the direction of operation.
- Mechanical Advantage: Spur gears offer a mechanical advantage in machinery. By utilizing gear ratios, spur gears can multiply or divide the force exerted on the input shaft. This mechanical advantage allows machinery to generate higher forces or achieve precise movements with reduced effort.
- Precision Positioning: Spur gears facilitate precise positioning in machinery. The accurate tooth engagement of spur gears ensures precise control over rotational motion, making them suitable for applications that require precise positioning or synchronization of components. Machinery such as CNC machines, robotics, and automation systems often rely on spur gears for accurate movement and positioning.
- Compact Design: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for machinery with space constraints. They can be arranged in-line, parallel, or at right angles, allowing for efficient power transmission in tight spaces. Their compactness enables machinery to be designed with smaller footprints and optimized layouts.
- Reliability and Durability: Spur gears are known for their reliability and durability in machinery. The direct tooth engagement and uniform load distribution result in efficient power transmission with reduced wear and stress concentration. When properly lubricated and maintained, spur gears can withstand heavy loads and operate reliably over extended periods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Spur gears are often cost-effective in machinery applications. Their simple design and ease of manufacturing contribute to lower production costs. Additionally, their high efficiency helps reduce energy consumption, resulting in potential long-term cost savings. The availability of spur gears in various sizes and materials further enhances their cost-effectiveness.
By utilizing spur gears in machinery, engineers and designers can achieve efficient power transmission, speed and torque control, directional versatility, mechanical advantage, precise positioning, compact design, reliability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. These advantages make spur gears a popular choice in a wide range of machinery applications across industries.
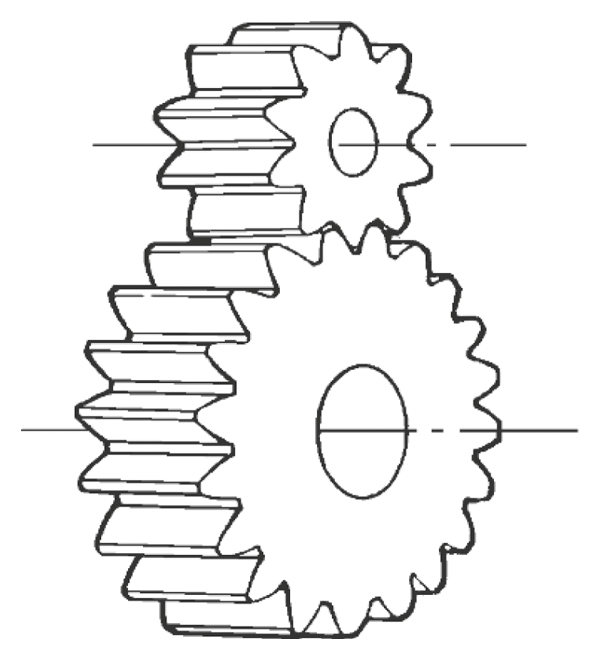
Are there different sizes and configurations of spur gears available?
Yes, there are various sizes and configurations of spur gears available to suit different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different options when it comes to sizes and configurations of spur gears:
Sizes: Spur gears come in a wide range of sizes to accommodate different torque and speed requirements. The size of a spur gear is typically specified by its pitch diameter, which is the diameter of the pitch circle. The pitch diameter determines the gear’s overall size and the spacing between the teeth. Spur gears can range from small gears used in precision instruments to large gears used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Module: Module is a parameter used to specify the size and spacing of the teeth on a spur gear. It represents the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth. Different module sizes are available to accommodate various gear sizes and applications. Smaller module sizes are used for finer tooth profiles and higher precision, while larger module sizes are used for heavier loads and higher torque applications.
Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on a spur gear can vary depending on the specific application. Gears with a higher number of teeth provide smoother operation and distribute the load more evenly, whereas gears with fewer teeth are typically used for higher speeds and compact designs.
Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is an important parameter that determines the shape and engagement of the teeth. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees. The selection of the pressure angle depends on factors such as load capacity, efficiency, and specific design requirements.
Profile Shift: Profile shift is a design feature that allows modification of the tooth profile to optimize the gear’s performance. It involves shifting the tooth profile along the gear’s axis, which can affect factors such as backlash, contact ratio, and load distribution. Profile shift can be positive (when the tooth profile is shifted towards the center of the gear) or negative (when the tooth profile is shifted away from the center).
Hub Configuration: The hub refers to the central part of the gear where it is mounted onto a shaft. Spur gears can have different hub configurations depending on the specific application. Some gears have a simple cylindrical hub, while others may have keyways, set screws, or other features to ensure secure and precise mounting.
Material and Coatings: Spur gears are available in various materials to suit different operating conditions and requirements. Common materials include steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic. Additionally, gears can be coated or treated with surface treatments such as heat treatment or coatings to enhance their wear resistance, durability, and performance.
Mounting Orientation: Spur gears can be mounted in different orientations depending on the application and space constraints. They can be mounted parallel to each other on parallel shafts, or they can be mounted at right angles using additional components such as bevel gears or shafts with appropriate bearings.
In summary, there is a wide range of sizes and configurations available for spur gears, including different pitch diameters, module sizes, number of teeth, pressure angles, profile shifts, hub configurations, materials, coatings, and mounting orientations. The selection of the appropriate size and configuration depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, load capacity, space constraints, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-04-25