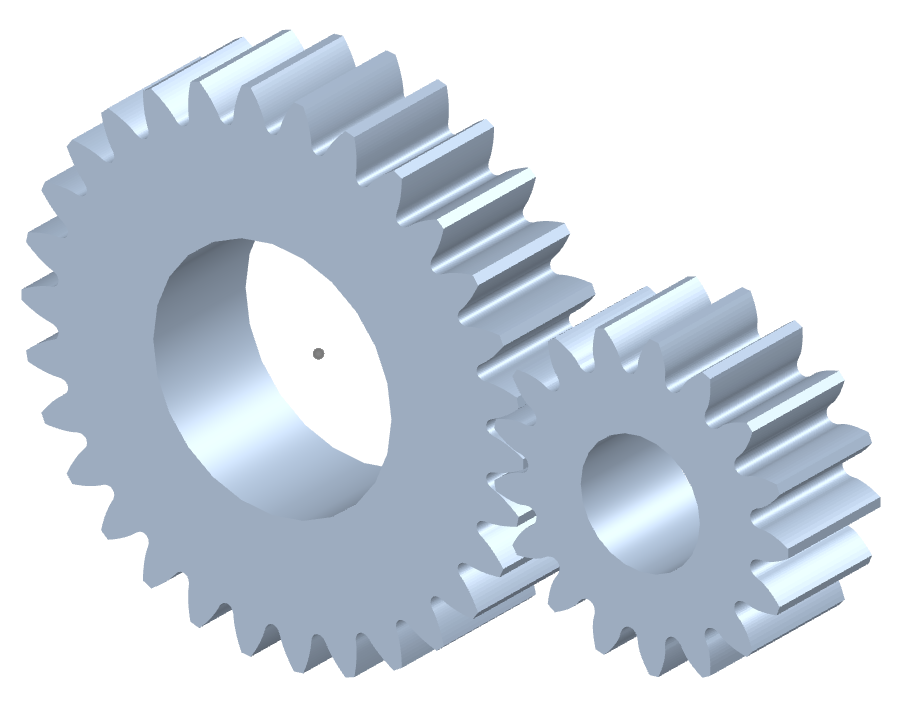
Product Description
Product Description
Gears, are widely used in conveyor system. According to the shape, there are spur gear, bevel gear, helical gear, pin gear, double gear and etc. According the using situation, gears involved in driving gears and drived gears. According to different using environment, there are different materials to choice, such as: HCPP, PVDF, PVC, POM, PA, PFA, PEEK, ETFE and etc. Main parameter for gears, there are: ID, OD, Teeth quantity, M, Length, Center circle. As we know: M*Teeth quantity=Center circle, so if you have any requirements, pls contact with us. We have professional design team, we can design drawing and choose suitable material for you, as your requirements.
Detailed Photos
Features
1- wear-resistant
2- corrosion resistance
3- transfer smooth
4- low transmission sound
5- easy to install and repair replacement
Product Parameters
| Name | Material | ID | Center Circle |
| Spur Gear | HCPP, PVDF, PVC, POM, PA, PFA, PEEK, ETFE and etc. | ID8, ID10, ID12, ID12.7, ID15, ID16 and etc. | 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 25, 30, 32, 35, 40, 48, 50 and etc. |
| Bevel Gear | |||
| Helical Gear | |||
| Pin Gear | |||
| Double Gear |
Note: If you need order gears, pls provide the data as the drawing:
Other Products
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are manufacturer.
Q: How to order ?
A: Normally you can order our products by using Made-in China platform or contacting representatives by Email.
After we receive your messages, we will help you to choose the right specifications and other inquiries.
Then we will send an proforma invoice to you via mail, it includes details of your order and our bank information.
After we received your payment by TT, we will ship your goods and we will send the invoice, packing list, and the express tracking number via mail.
Q: What is our term of trade ?
A: Usually we use EX WORKS. If you need other term of trade, please let us know.
Q: How to pay ?
A: We accept the payment by T/T (bank transfer) or pay through Made-in China platform.
Please inquire us about the details in advance.
Q: How are you going to deliver our goods ?
A: We can ship your goods either by air express (FedEx, DHL, UPS, TNT etc) or by sea.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | PCB Machine |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Injection Molding |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Plastic |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.4/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can spur gears be used in precision manufacturing equipment?
Yes, spur gears can be used in precision manufacturing equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Precision manufacturing equipment requires high accuracy, repeatability, and reliability to produce intricate and precise components. While other gear types like helical gears or bevel gears are commonly used in precision applications, spur gears can also be suitable in certain scenarios.
1. Low-Speed Applications:
Spur gears are well-suited for low-speed applications where high precision is required. In precision manufacturing equipment, such as milling machines, lathes, or grinding machines, where controlled and precise rotational motion is essential, spur gears can provide the necessary power transmission with accuracy.
2. Linear Actuators and Positioning Systems:
Spur gears can be used in linear actuators and positioning systems within precision manufacturing equipment. These systems require precise movement control, and spur gears can convert rotary motion into linear motion accurately. By incorporating precision-ground spur gears with proper backlash control, highly accurate positioning can be achieved.
3. Tooling Systems:
Spur gears are employed in tooling systems used in precision manufacturing equipment, such as indexing heads and rotary tables. These systems enable precise and repeatable positioning of workpieces or cutting tools. Spur gears with high precision tooth profiles and low backlash are utilized to ensure accurate tool positioning and consistent machining results.
4. Measuring and Inspection Equipment:
In precision manufacturing, gear systems are also utilized in measuring and inspection equipment. Spur gears can be incorporated into gear trains within instruments like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) or optical comparators to translate linear or rotary motion into precise measurement data. The gear systems in these instruments require minimal backlash and high accuracy to ensure accurate measurements.
5. Customized Gear Systems:
In some cases, precision manufacturing equipment may require custom-designed gear systems to meet specific application requirements. Spur gears can be tailored and optimized for these custom gear systems, taking into account factors like gear tooth profile, material selection, and gear geometry. This allows for the creation of highly precise and specialized gear systems.
While spur gears have advantages in precision manufacturing equipment, it’s important to consider their limitations. Due to their design, spur gears may produce more noise and vibration compared to other gear types. Additionally, they are generally not suitable for high-speed or high-torque applications that demand continuous and smooth power transmission.
Overall, spur gears can be successfully used in precision manufacturing equipment for specific applications that require low-speed, precise motion control, accurate positioning, and measurement capabilities. Proper gear selection, high-quality manufacturing, and careful system integration are key to achieving the desired precision and performance in these gear applications.
What is the purpose of using spur gears in machinery?
In machinery, spur gears serve several important purposes due to their unique characteristics and capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purpose of using spur gears in machinery:
- Power Transmission: Spur gears are primarily used for power transmission in machinery. They transfer rotational motion and torque from one shaft to another, allowing machinery to perform various tasks. By meshing the teeth of two or more spur gears together, power can be transmitted efficiently and reliably throughout the machinery.
- Speed Reduction or Increase: Spur gears enable speed reduction or increase in machinery. By combining gears with different numbers of teeth, the rotational speed can be adjusted to match the desired output speed. For example, using a larger gear driving a smaller gear can increase the speed output while reducing the torque, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the speed while increasing the torque.
- Torque Amplification: Spur gears can amplify torque in machinery. By using gears with different numbers of teeth, the torque can be adjusted to match the required output. For example, using a smaller gear driving a larger gear can increase the torque output while reducing the speed, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the torque while increasing the speed.
- Directional Control: Spur gears provide directional control in machinery. By meshing gears with opposite orientations, the rotational direction of the driven shaft can be reversed or changed. This directional control is crucial for machinery that requires bi-directional motion or needs to change the direction of operation.
- Mechanical Advantage: Spur gears offer a mechanical advantage in machinery. By utilizing gear ratios, spur gears can multiply or divide the force exerted on the input shaft. This mechanical advantage allows machinery to generate higher forces or achieve precise movements with reduced effort.
- Precision Positioning: Spur gears facilitate precise positioning in machinery. The accurate tooth engagement of spur gears ensures precise control over rotational motion, making them suitable for applications that require precise positioning or synchronization of components. Machinery such as CNC machines, robotics, and automation systems often rely on spur gears for accurate movement and positioning.
- Compact Design: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for machinery with space constraints. They can be arranged in-line, parallel, or at right angles, allowing for efficient power transmission in tight spaces. Their compactness enables machinery to be designed with smaller footprints and optimized layouts.
- Reliability and Durability: Spur gears are known for their reliability and durability in machinery. The direct tooth engagement and uniform load distribution result in efficient power transmission with reduced wear and stress concentration. When properly lubricated and maintained, spur gears can withstand heavy loads and operate reliably over extended periods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Spur gears are often cost-effective in machinery applications. Their simple design and ease of manufacturing contribute to lower production costs. Additionally, their high efficiency helps reduce energy consumption, resulting in potential long-term cost savings. The availability of spur gears in various sizes and materials further enhances their cost-effectiveness.
By utilizing spur gears in machinery, engineers and designers can achieve efficient power transmission, speed and torque control, directional versatility, mechanical advantage, precise positioning, compact design, reliability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. These advantages make spur gears a popular choice in a wide range of machinery applications across industries.

What is a spur gear and how does it work?
A spur gear is a type of cylindrical gear with straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. It is one of the most common and simplest types of gears used in various mechanical systems. Spur gears work by meshing together to transmit rotational motion and torque between two parallel shafts. Here’s a detailed explanation of spur gears and how they work:
A spur gear consists of two or more gears with cylindrical shapes and an equal number of teeth. These gears are mounted on parallel shafts, and their teeth mesh together to transfer rotational motion from one gear to another. The gear with power input is called the “drive gear” or “driver,” while the gear receiving the power output is called the “driven gear” or “follower.”
The key characteristics and components of spur gears include:
- Teeth: Spur gears have straight teeth that are cut parallel to the shaft axis. The teeth are evenly spaced around the circumference of the gear. The number of teeth determines the gear ratio and affects the speed and torque transmission between the gears.
- Pitch Diameter: The pitch diameter is the theoretical diameter of the gear at the point where the teeth mesh. It is determined by the number of teeth and the module or diametral pitch of the gear.
- Module or Diametral Pitch: The module is a parameter used in metric gear systems, while the diametral pitch is used in imperial gear systems. They define the tooth size and spacing of the gear. The module is the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth, while the diametral pitch is the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter.
- Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is the angle between the line tangent to the tooth profile at the pitch point and a line perpendicular to the gear axis. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees.
- Meshing: Spur gears mesh by engaging their teeth, creating a point or line contact between the contacting surfaces. The teeth transfer rotational motion and torque from the drive gear to the driven gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the drive gear and the driven gear. It defines the relationship between the input speed and the output speed. The gear ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the driven gear by the number of teeth on the drive gear.
- Operation: As the drive gear rotates, its teeth come into contact with the teeth of the driven gear. The contact between the teeth transfers rotational motion and torque from the drive gear to the driven gear. The meshing teeth maintain a constant speed ratio, allowing for the transmission of power between the shafts. The direction of rotation can be changed by meshing gears with an odd or even number of teeth.
Spur gears offer several advantages, including simplicity, ease of manufacture, efficiency, and reliability. They are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including machinery, automotive systems, appliances, power tools, and more.
In conclusion, spur gears are cylindrical gears with straight teeth that mesh together to transfer rotational motion and torque between parallel shafts. Their simple and efficient design makes them a popular choice for various mechanical systems.


editor by Dream 2024-05-09
China factory Ball Mill Segment Ring Gear Bull 35CrMo Casting Steel Custom Large Diameter Outer Spur Large Ring Gear gear patrol
Product Description
Key attributes
Other attributes
Applicable Industries
Building Material Shops, Manufacturing Plant, Machinery Repair Shops, Food & Beverage Factory, Retail, Construction works , Energy & Mining, Other
Weight (KG)
1200
Showroom Location
None
Video outgoing-inspection
Provided
Machinery Test Report
Provided
Marketing Type
New Product 2571
Warranty of core components
1 Year
Core Components
Gear
Place of CHINAMFG
ZheJiang , China
Condition
New
Warranty
1.5 years
Shape
Spur
Brand Name
TS
Material
Steel
Product Name
Large Diameter Ring Gears
Process
Milling,hobbing
Surface treatment
Grinding
Heat treatment
Q&T
Application
Industry machinery,transmission equipment
Standard
DIN ANSI ISO
Certificate
ISO 9001:2015
Module No.
Customized
Size
Customer’s Drawing
Quality
High level
Packaging and delivery
Packaging Details
Package adapting to CHINAMFG transport
Port
HangZhou, ZheJiang
Supply Ability
Supply Ability
15 Piece/Pieces per Month steel large spur gears
OUR WORKSHOPS
OUR EQUIPMENTS
Technology Process
|
Material |
Carbon steel,Alloy steel |
||
|
Structure |
Forging,casting |
||
|
Type of gear |
spur gear,helical gear,Planetary Gear |
||
|
Heat treatment |
Quenching and tempering |
||
|
Process |
forging, rough machining, QT, finish machining |
||
|
Main equipments |
hobbing,CNC machine |
||
|
Module |
up to 200 |
||
|
Precision of gear |
Grinding ISO Grade 5-7 & Hobbing ISO Grade 8-9 |
||
|
Inspection |
Raw material inspection, UT,physical property test,dimension inspect |
||
|
Application |
Mining machinery, mill, kiln and other equipment |
||
OUR CERTIFICATE
OUR CUSTOMER FEEDBACK
CONTACT
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Industry |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hb190-Hb300 |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 100/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do you calculate the efficiency of a spur gear?
Calculating the efficiency of a spur gear involves considering the power losses that occur during gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a gear system, power is transmitted from the driving gear (input) to the driven gear (output). However, due to various factors such as friction, misalignment, and deformation, some power is lost as heat and other forms of energy. The efficiency of a spur gear represents the ratio of the output power to the input power, taking into account these power losses.
Formula for Calculating Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency (η) of a spur gear can be calculated using the following formula:
η = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100%
Where:
η is the efficiency of the gear system expressed as a percentage.
Output Power is the power delivered by the driven gear (output) in the gear system.
Input Power is the power supplied to the driving gear (input) in the gear system.
Factors Affecting Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency of a spur gear is influenced by several factors, including:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the gear affects the efficiency. Well-designed gear teeth with accurate involute profiles can minimize friction and power losses during meshing.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication between the gear teeth reduces friction, wear, and heat generation, improving gear efficiency. Insufficient or inadequate lubrication can result in increased power losses and reduced efficiency.
- Gear Material: The selection of gear material affects efficiency. Materials with low friction coefficients and good wear resistance can help minimize power losses. Higher-quality materials and specialized gear coatings can improve efficiency.
- Gear Alignment and Meshing: Proper alignment and precise meshing of the gear teeth are essential for optimal efficiency. Misalignment or incorrect gear meshing can lead to increased friction, noise, and power losses.
- Bearing Friction: The efficiency of a gear system is influenced by the friction in the bearings supporting the gear shafts. High-quality bearings with low friction characteristics can contribute to improved gear efficiency.
- Load Distribution: Uneven load distribution across the gear teeth can result in localized power losses and reduced efficiency. Proper design and gear system configuration should ensure even load distribution.
Interpreting Gear Efficiency:
The calculated gear efficiency indicates the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output. For example, if a gear system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the input power is converted into useful output power, while the remaining 10% is lost as various forms of power dissipation.
It’s important to note that gear efficiency is not constant and can vary with operating conditions, lubrication quality, gear wear, and other factors. The calculated efficiency serves as an estimate and can be influenced by specific system characteristics and design choices.
By considering the factors affecting gear efficiency and implementing proper design, lubrication, and maintenance practices, gear efficiency can be optimized to enhance overall gear system performance and minimize power losses.

What is the lifespan of a typical spur gear?
The lifespan of a typical spur gear can vary significantly depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The lifespan of a spur gear is influenced by various factors, including:
- Operating Conditions: The conditions under which the spur gear operates greatly impact its lifespan. Factors such as the magnitude and frequency of the applied loads, operating temperature, speed, and lubrication quality play a significant role. Gears operating under heavy loads, high speeds, or harsh environments may experience higher wear and fatigue, potentially reducing their lifespan.
- Material Selection: The material used for constructing the spur gear affects its durability and lifespan. Spur gears are commonly made from materials such as steel, cast iron, bronze, or polymer composites. The specific material properties, including hardness, strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion, influence the gear’s ability to withstand the operating conditions and determine its lifespan.
- Quality of Manufacturing: The quality of manufacturing processes and techniques employed during the production of the spur gear can impact its lifespan. Gears manufactured with precision, accurate tooth profiles, and proper heat treatment are more likely to have longer lifespans compared to those with manufacturing defects or poor quality control.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in spur gears. Regular maintenance practices, including lubricant replacement, gear inspections, and addressing any issues promptly, can significantly extend the lifespan of the gears. Inadequate lubrication or neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear and failure.
- Load and Stress Distribution: The design and configuration of the gear system affect the load and stress distribution on the spur gears. Proper gear design, including tooth profile, number of teeth, and gear arrangement, helps ensure even load distribution and minimizes localized stress concentrations. Well-designed supporting components, such as bearings and shafts, also contribute to the overall lifespan of the gear system.
It is challenging to provide a specific lifespan for a typical spur gear since it depends on the aforementioned factors and the specific application. Spur gears can have lifespans ranging from several thousand to millions of operating cycles. Industrial gear systems often undergo regular inspections and maintenance, including gear replacement when necessary, to ensure safe and reliable operation.
It’s important to note that gear lifespan can be extended through proper care, maintenance, and adherence to recommended operating parameters. Regular inspections, monitoring of gear performance, and addressing any signs of wear or damage promptly can help maximize the lifespan of spur gears.
When assessing the lifespan of spur gears for a particular application, it is advisable to consult manufacturers, industry standards, and experts with expertise in gear design and maintenance for accurate estimations and recommendations.

What industries commonly use spur gears?
Spur gears find wide applications across various industries due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries that commonly use spur gears:
- Automotive Industry: The automotive industry extensively utilizes spur gears in various components and systems. They are commonly found in gearboxes, differentials, transmission systems, and engine timing mechanisms. Spur gears play a crucial role in transferring power and rotational motion between the engine, wheels, and other drivetrain components.
- Machinery and Manufacturing: Spur gears are widely employed in machinery and manufacturing equipment across different sectors. They are used in conveyor systems, machine tools, printing presses, textile machinery, packaging machinery, and a variety of industrial applications. Spur gears facilitate power transmission and motion control in these systems.
- Power Generation: Spur gears are essential in power generation systems such as wind turbines, hydroelectric turbines, and steam turbines. They are used to transmit power from the rotor to the generator, converting the rotational motion of the turbine blades into electricity. Spur gears enable efficient power transfer in these renewable energy systems.
- Robotics and Automation: Spur gears have significant applications in robotics and automation systems. They are used in robotic joints, actuators, and drive systems to control motion and transmit torque accurately and efficiently. Spur gears enable precise movement and force transmission in robotic applications.
- Aerospace and Aviation: The aerospace and aviation industries utilize spur gears in various applications. They can be found in aircraft landing gear systems, engine components, flight control systems, auxiliary power units (APUs), and other critical equipment. Spur gears play a vital role in transmitting power and controlling movement in these aerospace systems.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Spur gears are commonly used in the marine and shipbuilding industry. They find applications in propulsion systems, winches, steering mechanisms, and other equipment that require torque transmission and speed control. Spur gears enable efficient power transfer and maneuverability in marine vessels.
- Appliances and Household Equipment: Spur gears are present in numerous household appliances and equipment. They are used in washing machines, dishwashers, mixers, food processors, garage door openers, and many other appliances that require rotational motion and power transmission. Spur gears facilitate the efficient operation of these household devices.
- Power Tools: Spur gears are widely utilized in power tools such as drills, saws, grinders, and sanders. They enable the transmission of power from the motor to the tool’s cutting or grinding components, ensuring efficient and controlled operation. Spur gears contribute to the functionality and performance of power tools.
- Medical Equipment: Spur gears are used in various medical devices and equipment. They can be found in imaging systems, surgical robots, medical pumps, and other applications that require precise motion control and torque transmission. Spur gears play a critical role in the functioning of medical equipment.
- Clocks and Watches: Spur gears are a fundamental component in mechanical clocks and watches. They are responsible for accurate timekeeping by transferring rotational motion from the mainspring or oscillator to the hour, minute, and second hands. Spur gears have historical significance in timekeeping mechanisms.
These are just a few examples of the industries where spur gears are commonly used. Their simplicity, reliability, and efficiency make them a popular choice in a wide range of applications, enabling power transmission, motion control, and precise operation in diverse industrial sectors.


editor by Dream 2024-05-08
China supplier Low Noises Worm and Wormwheel OEM Steel Rack Spur Gear with high quality
Product Description
My advantages:
1. High quality materials, professional production, high-precision equipment. Customized design and processing;
2. Strong and durable, strong strength, large torque and good comprehensive mechanical properties;
3. High rotation efficiency, stable and smooth transmission, long service life, noise reduction and shock absorption;
4. Focus on gear processing for 20 years.
5. Carburizing and quenching of tooth surface, strong wear resistance, reliable operation and high bearing capacity;
6. The tooth surface can be ground, and the precision is higher after grinding.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
|---|---|
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Bevel Wheel |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Type: | Worm And Wormwheel |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you calculate the efficiency of a spur gear?
Calculating the efficiency of a spur gear involves considering the power losses that occur during gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation:
In a gear system, power is transmitted from the driving gear (input) to the driven gear (output). However, due to various factors such as friction, misalignment, and deformation, some power is lost as heat and other forms of energy. The efficiency of a spur gear represents the ratio of the output power to the input power, taking into account these power losses.
Formula for Calculating Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency (η) of a spur gear can be calculated using the following formula:
η = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100%
Where:
η is the efficiency of the gear system expressed as a percentage.
Output Power is the power delivered by the driven gear (output) in the gear system.
Input Power is the power supplied to the driving gear (input) in the gear system.
Factors Affecting Gear Efficiency:
The efficiency of a spur gear is influenced by several factors, including:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of the gear affects the efficiency. Well-designed gear teeth with accurate involute profiles can minimize friction and power losses during meshing.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication between the gear teeth reduces friction, wear, and heat generation, improving gear efficiency. Insufficient or inadequate lubrication can result in increased power losses and reduced efficiency.
- Gear Material: The selection of gear material affects efficiency. Materials with low friction coefficients and good wear resistance can help minimize power losses. Higher-quality materials and specialized gear coatings can improve efficiency.
- Gear Alignment and Meshing: Proper alignment and precise meshing of the gear teeth are essential for optimal efficiency. Misalignment or incorrect gear meshing can lead to increased friction, noise, and power losses.
- Bearing Friction: The efficiency of a gear system is influenced by the friction in the bearings supporting the gear shafts. High-quality bearings with low friction characteristics can contribute to improved gear efficiency.
- Load Distribution: Uneven load distribution across the gear teeth can result in localized power losses and reduced efficiency. Proper design and gear system configuration should ensure even load distribution.
Interpreting Gear Efficiency:
The calculated gear efficiency indicates the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output. For example, if a gear system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the input power is converted into useful output power, while the remaining 10% is lost as various forms of power dissipation.
It’s important to note that gear efficiency is not constant and can vary with operating conditions, lubrication quality, gear wear, and other factors. The calculated efficiency serves as an estimate and can be influenced by specific system characteristics and design choices.
By considering the factors affecting gear efficiency and implementing proper design, lubrication, and maintenance practices, gear efficiency can be optimized to enhance overall gear system performance and minimize power losses.

What is the purpose of using spur gears in machinery?
In machinery, spur gears serve several important purposes due to their unique characteristics and capabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of the purpose of using spur gears in machinery:
- Power Transmission: Spur gears are primarily used for power transmission in machinery. They transfer rotational motion and torque from one shaft to another, allowing machinery to perform various tasks. By meshing the teeth of two or more spur gears together, power can be transmitted efficiently and reliably throughout the machinery.
- Speed Reduction or Increase: Spur gears enable speed reduction or increase in machinery. By combining gears with different numbers of teeth, the rotational speed can be adjusted to match the desired output speed. For example, using a larger gear driving a smaller gear can increase the speed output while reducing the torque, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the speed while increasing the torque.
- Torque Amplification: Spur gears can amplify torque in machinery. By using gears with different numbers of teeth, the torque can be adjusted to match the required output. For example, using a smaller gear driving a larger gear can increase the torque output while reducing the speed, while the opposite arrangement can decrease the torque while increasing the speed.
- Directional Control: Spur gears provide directional control in machinery. By meshing gears with opposite orientations, the rotational direction of the driven shaft can be reversed or changed. This directional control is crucial for machinery that requires bi-directional motion or needs to change the direction of operation.
- Mechanical Advantage: Spur gears offer a mechanical advantage in machinery. By utilizing gear ratios, spur gears can multiply or divide the force exerted on the input shaft. This mechanical advantage allows machinery to generate higher forces or achieve precise movements with reduced effort.
- Precision Positioning: Spur gears facilitate precise positioning in machinery. The accurate tooth engagement of spur gears ensures precise control over rotational motion, making them suitable for applications that require precise positioning or synchronization of components. Machinery such as CNC machines, robotics, and automation systems often rely on spur gears for accurate movement and positioning.
- Compact Design: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for machinery with space constraints. They can be arranged in-line, parallel, or at right angles, allowing for efficient power transmission in tight spaces. Their compactness enables machinery to be designed with smaller footprints and optimized layouts.
- Reliability and Durability: Spur gears are known for their reliability and durability in machinery. The direct tooth engagement and uniform load distribution result in efficient power transmission with reduced wear and stress concentration. When properly lubricated and maintained, spur gears can withstand heavy loads and operate reliably over extended periods.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Spur gears are often cost-effective in machinery applications. Their simple design and ease of manufacturing contribute to lower production costs. Additionally, their high efficiency helps reduce energy consumption, resulting in potential long-term cost savings. The availability of spur gears in various sizes and materials further enhances their cost-effectiveness.
By utilizing spur gears in machinery, engineers and designers can achieve efficient power transmission, speed and torque control, directional versatility, mechanical advantage, precise positioning, compact design, reliability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. These advantages make spur gears a popular choice in a wide range of machinery applications across industries.

What are the benefits of using a spur gear mechanism?
Using a spur gear mechanism offers several benefits in various applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages of using a spur gear mechanism:
- Simplicity: Spur gear mechanisms are relatively simple in design, consisting of cylindrical gears with straight teeth. Their simplicity makes them easy to manufacture, assemble, and maintain. They have fewer components compared to other types of gear mechanisms, resulting in lower complexity and potentially reduced costs.
- Efficiency: Spur gears exhibit high efficiency in power transmission. The teeth of spur gears mesh directly, resulting in minimal energy loss during transmission. The simplicity of their tooth profile allows for efficient power transfer, making them an energy-efficient choice for many applications.
- Compactness: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. They can be arranged in-line, parallel to each other, or at right angles using additional components such as bevel gears. This flexibility in arrangement allows for efficient power transmission in tight spaces.
- Versatility: Spur gears are versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications. They are available in various sizes, configurations, and materials, allowing them to be tailored to specific needs. Spur gears can handle different torque and speed requirements, making them suitable for both low and high-speed applications.
- High-Speed Capability: Spur gears can achieve high rotational speeds due to their straightforward design and direct tooth engagement. They are capable of transmitting power efficiently at high speeds, making them suitable for applications that require rapid motion or high rotational velocities.
- Precise Positioning: Spur gears provide accurate positioning due to their precise tooth engagement. The straight teeth allow for precise control of rotational motion, making them suitable for applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics, machinery, and automation systems.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Spur gears are often cost-effective compared to other gear mechanisms. Their simple design and ease of manufacturing contribute to lower production costs. Additionally, their high efficiency helps reduce energy consumption, resulting in potential long-term cost savings.
- Reliability: Spur gears are known for their reliability and durability. The direct tooth engagement provides excellent load distribution, minimizing stress concentration and wear. When properly lubricated and maintained, spur gears can operate reliably for extended periods, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications.
- Wide Availability: Spur gears are widely available in the market, with various sizes, materials, and configurations to choose from. This availability ensures easy sourcing and replacement of gears when needed. Additionally, spur gears have been used for many years and have a well-established design and manufacturing process, leading to a robust supply chain.
These benefits make spur gear mechanisms a popular choice in numerous industries, including automotive, machinery, robotics, aerospace, appliances, and more. Their simplicity, efficiency, compactness, versatility, and reliability contribute to their widespread use in a wide range of applications.


editor by Dream 2024-05-08
China Custom OEM Large Worm Gear Spur Gear Helical Ring Gear and Pinion Truck Gear spiral bevel gear
Product Description
1) According to the different strength and performance, we choose the steel with strong compression;
2) Using Germany professional software and our professional engineers to design products with more reasonable size and better performance; 3) We can customize our products according to the needs of our customers,Therefore, the optimal performance of the gear can be exerted under different working conditions;
4) Quality assurance in every step to ensure product quality is controllable.
Product Paramenters
| DRIVEN GEAR |
NUMBER OF TEETH |
12 |
|
MODULE |
4.5 | |
|
LENTH |
372 | |
|
OUTER DIAMETER |
ø60 |
|
|
DIRECTION OF SPIRAL |
R |
|
|
ACCURACY OF SPLINE |
M27*1.5-6g | |
|
NUMBER OF SPLINE |
13/18 |
|
DRIVEN GEAR |
NUMBER OF TEETH |
56 |
|
OUTER DIAMETER |
ø251 |
|
|
DIAMETER OF INNER HOLE |
ø149 |
|
|
ACCURACY OF SCREW |
10-M10*1.25-6H | |
|
CENTER DISTANCE OF SCREW HOLE |
ø177 |
|
|
DIRECTION OF SPIRAL |
L |
Company Profiles
Our company,HangZhou CHINAMFG Gear co.,Ltd , specialized in Hypoid and spiral bevel gear used in Automotive industry, was foundeded in 1996, with registered capital 136,8 square meter, with building area of 72,000 square meters. More than 500 employees work in our company.
We own more than 560 high-precise machining equipments, 10 Klingelnberg Oerlikon gear production lines, 36 Gleason gear production lines, 5 forging production lines 2 german Aichilin and 5 CHINAMFG CHINAMFG advanced automatic continuous heat treatment production lines. With the introducing the advanced Oerlikon C50 and P65 measuring center, we enhence our technology level and improve our product quality a lot. We offer better quality and good after-sale service with low price, which insure the good reputation. With the concept of “for the people, by technology, creativity, for the society, transfering friendship, honest”, we are trying to provice the world-top level product.
Our aim is: CHINAMFG Gear,world class, Drive the world.
According to the different strength and performance, we choose the steel with strong compression;Using Germany professional software and our professional engineers to design products with more reasonable size and better performance;We can customize our products according to the needs of our customers,Therefore, the optimal performance of the gear can be exerted under different working conditions;Quality assurance in every step to ensure product quality is controllable.
Our company had full quality management system and had been certified by ISO9001:2000, QS-9000:1998, ISO/TS16949 , which insure the entrance of international market.
Certification & honors
Packaging & Shipping
Packaging Detail:standard package(carton ,wooden pallet).
Shipping:Support Sea freight. Accept FOB,EXW,FAS,DES.
Cooperative customers
HangZhou CHINAMFG Gear Co., Ltd. adheres to the concept of “people-oriented, prosper with science and technology; create high-quality products, contribute to the society; turn friendship, and contribute sincerely”, and will strive to create world automotive axle spiral bevel gear products.
1.Do you provide samples?
Yes,we can offer free sample but not pay the cost of freight.
2.What about OEM?
Yes,we can do OEM according to your requirements.
3.How about after-sales service?
We have excellent after-sales service if you have any quanlity problem,you can contact us anytime.
4.What about package?
Stardard package or customized package as requirements.
5.How to ensure the quanlity of the products?
We can provide raw meterial report,metallographic examination and the accuracy testing etc.
6.How long is your delivery time?
Genarally it is 4-7 days.If customized it will be take 20 days according to your quantity. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cast Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Type: | Bevel Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 60/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with spur gears?
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears involves modifying or replacing certain components to incorporate spur gears into the system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Evaluate the Existing System:
Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to determine its design, function, and limitations. Identify the specific components that need to be retrofitted with spur gears and understand how the system operates.
2. Design Considerations:
Based on the evaluation, consider the design considerations for integrating spur gears into the system. This includes factors such as gear size, tooth profile, gear material, gear ratio, and torque requirements. Determine the specific gear specifications that are compatible with the existing system.
3. Gear Selection:
Select the appropriate spur gears that meet the required specifications. Consider factors such as gear quality, load capacity, noise level, efficiency, and compatibility with the existing system components. Choose gears from reputable manufacturers or consult with a gear specialist for guidance.
4. Gear Positioning and Alignment:
Determine the optimal positioning and alignment of the spur gears within the existing system. This involves identifying the gear locations, shaft connections, and ensuring proper alignment with other components such as bearings and couplings. Accurate positioning and alignment are crucial for efficient gear operation and longevity.
5. Modification or Replacement:
Based on the design considerations and gear selection, proceed with the necessary modifications or replacements. This may involve removing existing components, such as gears with different tooth profiles, and replacing them with the selected spur gears. Ensure proper installation and secure attachment of the new gears.
6. Lubrication and Maintenance:
Implement appropriate lubrication practices for the newly retrofitted spur gears. Consult gear manufacturers’ recommendations for lubricant type, quantity, and maintenance intervals. Proper lubrication ensures smooth gear operation, reduces wear, and extends gear life.
7. Testing and Validation:
After the retrofitting process, conduct thorough testing and validation of the modified system. Verify that the spur gears are functioning as intended, ensuring proper engagement, smooth operation, and adequate load handling. Address any issues or discrepancies discovered during testing.
8. Documentation and Training:
Create documentation detailing the retrofitting process, including gear specifications, installation procedures, and maintenance requirements. This documentation serves as a reference for future maintenance and helps ensure consistent gear performance. Additionally, provide training to relevant personnel on the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the retrofitted system.
Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears requires careful planning, proper gear selection, precise installation, and thorough testing. By following these steps and considering the specific requirements of the system, it is possible to successfully incorporate spur gears and enhance the performance and functionality of the mechanical system.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of using spur gears?
Spur gears offer several advantages and disadvantages when used in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of using spur gears:
Advantages of Spur Gears:
- Simplicity: Spur gears have a simple and straightforward design, consisting of cylindrical gears with straight teeth. Their simplicity facilitates ease of manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Efficiency: Spur gears are highly efficient in transmitting power from one shaft to another. They have minimal sliding friction between the gear teeth, resulting in high mechanical efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their simple design and ease of production, spur gears are generally more cost-effective compared to other types of gears. They are widely available and can be manufactured in large quantities at a reasonable cost.
- Compactness: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. They can be arranged in parallel or stacked configurations to achieve the desired gear ratios within a confined space.
- High Load Capacity: Spur gears can handle high load capacities and transmit substantial amounts of torque. Their teeth are designed to distribute the load evenly across the gear face, resulting in improved load-bearing capabilities.
- Precision: Spur gears provide precise and predictable motion due to the simplicity of their tooth engagement. This makes them suitable for applications that require accurate positioning and synchronization.
Disadvantages of Spur Gears:
- Noisy Operation: Spur gears can produce noise during operation, especially at high speeds. The engagement of the gear teeth generates impact and vibration, resulting in noise that may require additional measures to mitigate.
- Axial Thrust: Spur gears generate axial thrust forces along the gear shafts due to the parallel arrangement of their teeth. This thrust must be properly managed using thrust bearings or other means to prevent excessive axial loading on the gear shafts.
- Limited Speed Ratio: Spur gears are primarily designed for applications with moderate speed ratios. They are less suitable for high-speed applications due to the limitations imposed by the tooth engagement and potential for increased noise and vibration.
- Unidirectional Operation: Spur gears are typically designed for unidirectional power transmission. Reversing the direction of rotation can cause noise, impact, and increased wear due to the abrupt change in tooth engagement.
- Prone to Wear: The sliding contact between the gear teeth in spur gears can result in wear over time, especially under heavy loads or inadequate lubrication. Regular maintenance and proper lubrication are necessary to minimize wear and extend gear life.
It’s important to consider these advantages and disadvantages when selecting gear types for specific applications. While spur gears are well-suited for many applications, other gear types, such as helical gears or bevel gears, may be more suitable in certain situations depending on the requirements and operating conditions.

How do you choose the right size spur gear for your application?
Choosing the right size spur gear for your application requires careful consideration of various factors. Here’s a detailed explanation of the steps involved in selecting the appropriate size spur gear:
- Determine the Required Torque: Start by determining the torque requirements of your application. Calculate or estimate the maximum torque that the gear will need to transmit. Consider factors such as the power input, speed, and load conditions to determine the required torque.
- Identify the Speed Requirements: Determine the desired rotational speed or RPM (revolutions per minute) for your application. This will help in selecting a gear with the appropriate pitch diameter and tooth configuration to achieve the desired speed.
- Consider the Load Conditions: Evaluate the expected load conditions, including the magnitude and direction of the load. Determine if the load is constant or variable, and if it involves shock loads or cyclic loading. This will impact the gear’s durability and load-carrying capacity.
- Calculate the Pitch Diameter: Based on the torque and speed requirements, calculate the pitch diameter of the spur gear. The pitch diameter is determined by the formula: Pitch Diameter = (2 x Torque) / (Pressure Angle x Allowable Tooth Shear Stress).
- Select the Module Size: Choose an appropriate module size based on the gear size and application requirements. The module size determines the tooth size and spacing. Smaller module sizes are used for fine tooth profiles and higher precision, while larger module sizes are suitable for heavier loads and higher torque applications.
- Determine the Number of Teeth: Based on the pitch diameter and module size, calculate the number of teeth required for the gear. Ensure that the gear has an adequate number of teeth for smooth operation, load distribution, and sufficient contact ratio.
- Consider Space Constraints: Evaluate the available space and mounting requirements in your application. Ensure that the selected gear size can fit within the available space and can be properly mounted on the shaft or gearbox.
- Choose the Material: Consider the operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and presence of corrosive substances, to select the appropriate material for the spur gear. Common materials include steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic. Choose a material that offers the necessary strength, wear resistance, and durability for your specific application.
- Consider Additional Design Features: Depending on your application requirements, you may need to consider additional design features such as profile shift, hub configuration, and surface treatments. Profile shift can optimize gear performance, while specific hub configurations and surface treatments may be necessary for proper mounting and enhanced durability.
It’s important to note that gear selection is a complex process, and it may require consultation with gear manufacturers or experts in the field. They can provide guidance based on their expertise and assist in selecting the most suitable spur gear for your specific application.
By thoroughly considering factors such as torque requirements, speed, load conditions, pitch diameter, module size, number of teeth, space constraints, material selection, and additional design features, you can choose the right size spur gear that meets the demands of your application in terms of performance, durability, and efficiency.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07
China high quality Customized High Precision Hot Forging Spur Gear with Great quality
Product Description
We are a professional company in bulk material handling, transportation, storage, processing, accessory equipment design, integration and manufacturing. We can provide a complete set of solutions. Thank you for reading the information and welcome to purchase! Welcome to agent distribution!
Brief introduction of the company’s manufacturing capacity
The company’s headquarters, technology and sales are located in Lingang New Area of China (ZheJiang ) pilot free trade zone,The company’s manufacture base is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis. county, ZHangZhoug Province, which is known as “the most beautiful county in China”. It is 65 kilometers away from HangZhou city and 60 kilometers away from Qiandao Lake. The transportation to Xihu (West Lake) Dis. county from other places is very convenient. No matter by railway, highway or waterway. The manufacture base has a total plant area of around 30000 square CHINAMFG and workshop is equipped with more than 300 sets of various advance manufacture equipment, including 20 sets of CNC precision vertical lathe MODEL: SMVTM12000×50/150, CNC vertical lathe MODEL:DVT8000×30/32, CNC horizontal lathe, MODEL: CK61315×125/32, CNC horizontal lathe MODEL:CK61200×80/32, CNC Grounding boring and milling machine MODEL:TJK6920,etc.Most of the parts are machined by using CNC machine equipment. Theis is a hot treatment CHINAMFG with size 10.5m×8m×8m. The manufacture base also equipped with lifting capacity of 25t, 50t, 100t, 200t overhead crane to handle heavy workpiece and assembly work.
Metalworking equipment
| Name of equipment | Model number | Quantity | SCOPE of application | |
| A | Lathes | |||
| 1 | Vertical Lathe | Numerical control | 1 | Φ 12000 |
| 2 | Vertical Lathe | Numerical control | 1 | Φ 8000 |
| 3 | Vertical Lathe | 1 | Φ 1600 | |
| 4 | Vertical Lathe | C5112A | 1 | Ф 1250 |
| 5 | Horizontal Lathe | Numerical control | 1 | CK61315×12×100T |
| 6 | Horizontal Lathe | CW61200 | 1 | Ф 2000×8000 |
| 7 | Horizontal Lathe | CW61160 | 1 | Ф 1600×6500 |
| 8 | Horizontal Lathe | CW6180 | 2 | Ф 800×3000 |
| 9 | Horizontal Lathe | CW61125 | 2 | Ф 1250×5000 |
| 10 | Horizontal Lathe (remodel) | CW62500 | 2 | Ф 2800×6000 |
| 11 | Common Lathe | CY6140 | 3 | Ф 400×1000 |
| 12 | Common Lathe | CA6140 | 3 | Ф 400×1500 |
| 13 | Common Lathe | C620 | 2 | Ф 400×1400 |
| 14 | Common Lathe | C616 | 1 | Ф 320×1000 |
| 15 | Common Lathe | C650 | 1 | Ф 650×2000 |
| B | Drilling machine | |||
| 1 | Radial drilling machine | Z3080 | 3 | Ф 80×2500 |
| 2 | Radial drilling machine | Z3040 | 2 | Ф 60×1600 |
| 3 | Universal drilling machine | ZW3725 | 3 | Ф 25×880 |
| C | Planing machine | |||
| 1 | Shaper | B665 | 1 | L650 |
| 2 | Hydraulic Shaper | B690 | 1 | L900 |
| 3 | Gantry Planer | HD–16 | 1 | L10000×B1600 |
| D | Milling Machine | |||
| 1 | 4 Coordinate Milling Machine | Numerical control | 1 | 2500×4000 |
| 2 | Gantry milling machine | Numerical contro | 1 | 16mx5mx3m |
| 3 | Gantry milling machine | Numerical contro | 1 | 12mx4mx2.5m |
| 4 | Gantry milling and boring machine | Numerical contro | 1 | Φ 250 |
| 5 | Vertical Milling Machine | XS5054 | 1 | 1600×400 |
| 6 | Horizontal Milling Machine | C62W | 1 | 1250×320 |
| 7 | Horizontal Milling Machine | X60 | 1 | 800×200 |
| 8 | Gantry milling machine | X2014J | 1 | L4000×B1400 |
| 9 | Gantry milling machine | X2571J | 1 | L3000×B1000 |
| 10 | Floor end milling | TX32-1 | 1 | L1500×H800 |
| E | Grinding machine | |||
| 1 | External Grinder | M131W | 1 | Ф 300×1000 |
| 2 | External Grinder | M1432B | 1 | Ф 320×15000 |
| 3 | Surface Grinder | M7130 | 1 | L 1000×300 |
| 4 | Tool grinder | M6571C | 1 | Ф 250 |
| F | Boring machine | |||
| 1 | Floor-standing milling and boring machine | TJK6920 | 1 | X12000 × Y4500 × Z1000 |
| 2 | Boring machine | TSPX619 | 1 | Ф 1000 |
| 3 | Boring machine | T616 | 1 | Ф 800 |
| 4 | Boring machine | T611 | 1 | Ф 800 |
| G | Slotted bed | |||
| 1 | Slotted bed | B5032 | 1 | H320 |
| H | Other machine tools | |||
| 1 | Gear hobbing machine | Y3150 | 1 | Ф 500 M=6 |
| 2 | Hacksaw machine | G7571 | 1 | Ф 220 |
Products and services available
Material handling equipment
Storage equipment
Conveying equipment
Feeding equipment
Component of conveying system
Belt conveyor parts
Large and medium sized finishing parts
If you need above products, please contact us!
ZheJiang Sunshine Industrial Technology Co. , Ltd.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Marine, Toy, Agricultural Machinery, Car, Customization |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Customization |
| Gear Position: | Customization |
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What are the environmental considerations when using spur gears?
When using spur gears, there are several environmental considerations to keep in mind. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential for the efficient and reliable operation of spur gears. However, the choice of lubricant can have environmental implications. It is important to select lubricants that are environmentally friendly, such as biodegradable or non-toxic lubricants. These lubricants minimize the risk of contaminating soil, water, or air during gear operation or maintenance.
2. Material Selection:
The choice of gear materials can also have environmental implications. Opting for materials that are recyclable or made from recycled content can reduce the environmental impact associated with gear production and end-of-life disposal. Additionally, selecting materials with low toxicity and minimal environmental harm during their lifecycle is important for sustainable gear manufacturing.
3. Energy Efficiency:
Efficient gear design and operation contribute to energy conservation and decreased environmental impact. By optimizing gear design, tooth profiles, and lubrication, it is possible to minimize power losses and increase overall gear system efficiency. This, in turn, reduces energy consumption and the associated environmental footprint.
4. Noise and Vibration:
Spur gears can generate noise and vibration during operation, which can have environmental implications, especially in noise-sensitive or residential areas. Implementing noise reduction measures such as gear tooth profiling, proper lubrication, and noise dampening techniques can help minimize the environmental impact of gear-induced noise and vibration.
5. Maintenance and End-of-Life Disposal:
Proper maintenance practices play a crucial role in minimizing the environmental impact of spur gears. Regular inspection, cleaning, and lubrication can prolong gear life, reduce the need for replacements, and minimize waste generation. Additionally, when spur gears reach the end of their life cycle, it is important to dispose of them responsibly, considering recycling options and proper waste management practices.
6. Environmental Regulations and Compliance:
When using spur gears, it is crucial to stay informed about relevant environmental regulations and standards. Different regions or industries may have specific requirements regarding lubricants, materials, noise emissions, or waste disposal. Adhering to these regulations ensures compliance and minimizes the environmental impact of gear usage.
7. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA):
Conducting a life cycle assessment of spur gears helps evaluate their overall environmental impact. LCA considers the environmental implications of gear production, use, maintenance, and disposal. It provides insights into potential environmental hotspots, allowing for targeted improvements in gear design, material selection, and operational practices.
By considering these environmental considerations and adopting sustainable practices throughout the life cycle of spur gears, it is possible to minimize their environmental impact and promote more environmentally friendly gear systems.

How do you install a spur gear system?
Installing a spur gear system involves several steps to ensure proper alignment, engagement, and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to install a spur gear system:
- Preparation: Before installation, gather all the necessary components, including the spur gears, shafts, bearings, and any additional mounting hardware. Ensure that the gear system components are clean and free from debris or damage.
- Shaft Alignment: Proper shaft alignment is crucial for the smooth operation of a spur gear system. Ensure that the shafts on which the gears will be mounted are aligned accurately and parallel to each other. This can be achieved using alignment tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems. Adjust the shaft positions as needed to achieve the desired alignment.
- Positioning the Gears: Place the spur gears on the respective shafts in the desired configuration. Ensure that the gears are positioned securely and centered on the shafts. For shafts with keyways, align the gears with the key and ensure a proper fit. Use any necessary mounting hardware, such as set screws or retaining rings, to secure the gears in place.
- Checking Gear Engagement: Verify that the teeth of the gears mesh properly with each other. The gear teeth should align accurately and smoothly without any excessive gaps or interference. Rotate the gears by hand to ensure smooth and consistent meshing throughout their rotation. If any misalignment or interference is observed, adjust the gear positions or shaft alignment accordingly.
- Bearing Installation: If the spur gear system requires bearings to support the shafts, install the bearings onto the shafts. Ensure that the bearings are the correct size and type for the application. Press or slide the bearings onto the shafts until they are seated securely against any shoulder or bearing housing. Use appropriate methods and tools to prevent damage to the bearings during installation.
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable lubricant to the gear teeth and bearings to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction. Refer to the gear manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate lubrication type and amount. Proper lubrication helps minimize wear, noise, and heat generation in the gear system.
- Final Inspection: Once the gears, shafts, and bearings are installed, perform a final inspection of the entire spur gear system. Check for any unusual noises, misalignment, or binding during manual rotation. Verify that the gears are securely mounted, shafts are properly aligned, and all fasteners are tightened to the specified torque values.
It’s important to follow the specific installation instructions provided by the gear manufacturer to ensure proper installation and operation. Additionally, consult any applicable industry standards and guidelines for gear system installation.
By carefully following these installation steps, you can ensure a well-aligned and properly functioning spur gear system in your machinery or equipment.
What are the applications of spur gears?
Spur gears find a wide range of applications in various mechanical systems due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. These gears are commonly used in numerous industries and equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of spur gears:
- Automotive Industry: Spur gears are extensively used in automobiles for power transmission applications. They are employed in gearboxes, differentials, and transmission systems to transfer torque and rotational motion between the engine, wheels, and other components.
- Machinery and Manufacturing: Spur gears are widely utilized in machinery and manufacturing equipment. They play a crucial role in conveyor systems, machine tools, printing presses, textile machinery, packaging machinery, and various other industrial applications.
- Power Generation: Spur gears are employed in power generation systems such as wind turbines, hydroelectric turbines, and steam turbines. They help convert the rotational motion of the turbine blades into electricity by transmitting power from the rotor to the generator.
- Robotics and Automation: Spur gears are commonly used in robotics and automation systems. They are utilized in robotic joints, actuators, and drive systems to control motion and transmit torque accurately and efficiently.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Spur gears are found in various aerospace and aviation applications. They are used in aircraft landing gear systems, engine components, flight control systems, and auxiliary power units (APUs) to transmit power and control movement.
- Marine and Shipbuilding: Spur gears have applications in the marine and shipbuilding industry. They are used in propulsion systems, winches, steering mechanisms, and other equipment that require torque transmission and speed control.
- Appliances and Household Equipment: Spur gears are present in numerous household appliances and equipment. They are found in washing machines, dishwashers, mixers, food processors, garage door openers, and many other appliances that require rotational motion and power transmission.
- Power Tools: Spur gears are utilized in power tools such as drills, saws, grinders, and sanders. They help transmit power from the motor to the tool’s cutting or grinding components, enabling efficient operation.
- Medical Equipment: Spur gears are used in various medical devices and equipment. They can be found in imaging systems, surgical robots, medical pumps, and other applications that require precise motion control and torque transmission.
- Clocks and Watches: Spur gears are an essential component in mechanical clocks and watches. They are responsible for accurate timekeeping by transferring rotational motion from the mainspring or oscillator to the hour, minute, and second hands.
These are just a few examples of the broad range of applications where spur gears are utilized. Their simplicity, reliability, and ability to transmit power and motion efficiently make them a popular choice in various industries and equipment.


editor by Dream 2024-05-07
China supplier High Precision Miniature Spur Gear/Double Spur Gear/Small Spur Gear in China with Great quality
Product Description
Precision gear used for Motor
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price – quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
| Specificate | Material | Hardness |
| Z13 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z16 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z18 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z20 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z26 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Z28 | Steel | HRC35-40 |
| Custom diemension according to drawings | Steel | HRC35-40 |
Workshop:
Inspection machine:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | Internal Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Spur Gear |
| Material: | Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
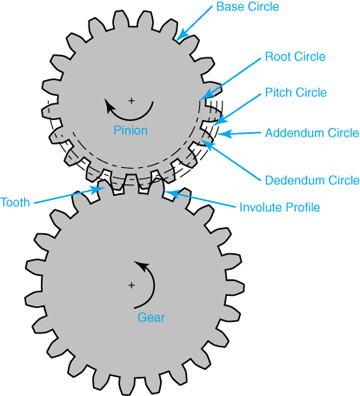
Can spur gears be used in automotive applications?
Yes, spur gears can be used in automotive applications. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Spur gears are one of the simplest and most commonly used types of gears. They consist of cylindrical teeth that are parallel to the gear axis and mesh with each other to transmit power and motion. While other gear types like helical gears or bevel gears are often preferred in certain automotive applications, spur gears still find their place in various automotive systems and components.
1. Transmissions:
Spur gears are commonly found in manual transmissions, especially in lower gears. They are used to achieve a direct and efficient power transfer between the engine and the wheels. Spur gears in transmissions are designed to handle high torque loads and provide reliable performance.
2. Differential:
In automotive differentials, which distribute power between the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, spur gears are often employed. They are used in the differential gear train to transfer torque from the driveshaft to the wheels. The simplicity and robustness of spur gears make them suitable for this application.
3. Starter Motors:
Spur gears are commonly used in starter motors to crank the engine when starting a vehicle. They provide high torque and efficient power transmission to rotate the engine’s crankshaft and initiate the combustion process. Starter motor spur gears are designed to handle the initial load and engage smoothly with the engine’s flywheel.
4. Timing Systems:
In automotive timing systems, where precise synchronization of engine components is crucial, spur gears can be used. They are employed in timing belts or chains to drive the camshafts, ensuring proper valve timing and engine performance. Spur gears in timing systems contribute to accurate and reliable engine operation.
5. Accessories and Auxiliary Components:
Spur gears are also utilized in various automotive accessories and auxiliary components. They can be found in power window mechanisms, windshield wipers, power steering systems, and other mechanisms that require controlled and synchronized motion. Spur gears provide cost-effective and efficient power transmission for these applications.
It’s important to note that while spur gears have their advantages, they also have certain limitations. They can generate more noise and vibration compared to gears with helical or bevel tooth profiles. Additionally, spur gears are not as suitable for high-speed or high-torque applications as other gear types.
Overall, spur gears have a significant presence in automotive applications, particularly in manual transmissions, differentials, starter motors, timing systems, and various auxiliary components. Their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a viable choice for specific automotive gear applications.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of using spur gears?
Spur gears offer several advantages and disadvantages when used in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the advantages and disadvantages of using spur gears:
Advantages of Spur Gears:
- Simplicity: Spur gears have a simple and straightforward design, consisting of cylindrical gears with straight teeth. Their simplicity facilitates ease of manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
- Efficiency: Spur gears are highly efficient in transmitting power from one shaft to another. They have minimal sliding friction between the gear teeth, resulting in high mechanical efficiency.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Due to their simple design and ease of production, spur gears are generally more cost-effective compared to other types of gears. They are widely available and can be manufactured in large quantities at a reasonable cost.
- Compactness: Spur gears have a compact design, making them suitable for applications where space is limited. They can be arranged in parallel or stacked configurations to achieve the desired gear ratios within a confined space.
- High Load Capacity: Spur gears can handle high load capacities and transmit substantial amounts of torque. Their teeth are designed to distribute the load evenly across the gear face, resulting in improved load-bearing capabilities.
- Precision: Spur gears provide precise and predictable motion due to the simplicity of their tooth engagement. This makes them suitable for applications that require accurate positioning and synchronization.
Disadvantages of Spur Gears:
- Noisy Operation: Spur gears can produce noise during operation, especially at high speeds. The engagement of the gear teeth generates impact and vibration, resulting in noise that may require additional measures to mitigate.
- Axial Thrust: Spur gears generate axial thrust forces along the gear shafts due to the parallel arrangement of their teeth. This thrust must be properly managed using thrust bearings or other means to prevent excessive axial loading on the gear shafts.
- Limited Speed Ratio: Spur gears are primarily designed for applications with moderate speed ratios. They are less suitable for high-speed applications due to the limitations imposed by the tooth engagement and potential for increased noise and vibration.
- Unidirectional Operation: Spur gears are typically designed for unidirectional power transmission. Reversing the direction of rotation can cause noise, impact, and increased wear due to the abrupt change in tooth engagement.
- Prone to Wear: The sliding contact between the gear teeth in spur gears can result in wear over time, especially under heavy loads or inadequate lubrication. Regular maintenance and proper lubrication are necessary to minimize wear and extend gear life.
It’s important to consider these advantages and disadvantages when selecting gear types for specific applications. While spur gears are well-suited for many applications, other gear types, such as helical gears or bevel gears, may be more suitable in certain situations depending on the requirements and operating conditions.

What is a spur gear and how does it work?
A spur gear is a type of cylindrical gear with straight teeth that are parallel to the gear axis. It is one of the most common and simplest types of gears used in various mechanical systems. Spur gears work by meshing together to transmit rotational motion and torque between two parallel shafts. Here’s a detailed explanation of spur gears and how they work:
A spur gear consists of two or more gears with cylindrical shapes and an equal number of teeth. These gears are mounted on parallel shafts, and their teeth mesh together to transfer rotational motion from one gear to another. The gear with power input is called the “drive gear” or “driver,” while the gear receiving the power output is called the “driven gear” or “follower.”
The key characteristics and components of spur gears include:
- Teeth: Spur gears have straight teeth that are cut parallel to the shaft axis. The teeth are evenly spaced around the circumference of the gear. The number of teeth determines the gear ratio and affects the speed and torque transmission between the gears.
- Pitch Diameter: The pitch diameter is the theoretical diameter of the gear at the point where the teeth mesh. It is determined by the number of teeth and the module or diametral pitch of the gear.
- Module or Diametral Pitch: The module is a parameter used in metric gear systems, while the diametral pitch is used in imperial gear systems. They define the tooth size and spacing of the gear. The module is the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth, while the diametral pitch is the number of teeth per inch of pitch diameter.
- Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is the angle between the line tangent to the tooth profile at the pitch point and a line perpendicular to the gear axis. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees.
- Meshing: Spur gears mesh by engaging their teeth, creating a point or line contact between the contacting surfaces. The teeth transfer rotational motion and torque from the drive gear to the driven gear.
- Gear Ratio: The gear ratio is determined by the number of teeth on the drive gear and the driven gear. It defines the relationship between the input speed and the output speed. The gear ratio can be calculated by dividing the number of teeth on the driven gear by the number of teeth on the drive gear.
- Operation: As the drive gear rotates, its teeth come into contact with the teeth of the driven gear. The contact between the teeth transfers rotational motion and torque from the drive gear to the driven gear. The meshing teeth maintain a constant speed ratio, allowing for the transmission of power between the shafts. The direction of rotation can be changed by meshing gears with an odd or even number of teeth.
Spur gears offer several advantages, including simplicity, ease of manufacture, efficiency, and reliability. They are commonly used in a wide range of applications, including machinery, automotive systems, appliances, power tools, and more.
In conclusion, spur gears are cylindrical gears with straight teeth that mesh together to transfer rotational motion and torque between parallel shafts. Their simple and efficient design makes them a popular choice for various mechanical systems.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
China OEM Hardened Tooth Surface External OEM Hunting Spur Wheel Shaft Cement Mixer Helical Gear gear ratio calculator
Product Description
Product introduction
| Modulo | Above 0.8 |
| Numero di Denti | Above 9teeth |
| Angolo d’Elica Helix Angle | Up to 45 |
| bore diameter | Above 6mm |
| axial length | Above 9mm |
| Gear model | Customized gear accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| Processing machine | CNC machine |
| Material | 20CrMnTi/ 20CrMnMo/ 42CrMo/ 45#steel/ 40Cr/ 20CrNi2MoA/304 stainless steel |
| Heat treattment | Carburizing and quenching/ Tempering/ Nitriding/ Carbonitriding/ Induction hardening |
| Hardness | 35-64HRC |
| Qaulity standerd | GB/ DIN/ JIS/ AGMA |
| Accuracy class | 5-8 class |
| Shipping | Sea shipping/ Air shipping/ Express |
My advantages:
1. High quality materials, professional production, high-precision equipment. Customized design and processing;
2. Strong and durable, strong strength, large torque and good comprehensive mechanical properties;
3. High rotation efficiency, stable and smooth transmission, long service life, noise reduction and shock absorption;
4. Focus on gear processing for 20 years.
5. Carburizing and quenching of tooth surface, strong wear resistance, reliable operation and high bearing capacity;
6. The tooth surface can be ground, and the precision is higher after grinding.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
|---|---|
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Cut Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Bevel Wheel |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Type: | Worm And Wormwheel |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing spur gears?
Designing and manufacturing spur gears involve several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance and reliability. Here’s a detailed explanation of the potential challenges in designing and manufacturing spur gears:
- Gear Tooth Design: Designing the gear tooth profile is a critical aspect of gear design. Achieving the desired tooth shape, pressure angle, and tooth thickness distribution while considering factors such as load capacity, durability, and noise generation can be challenging. Iterative design processes, computer-aided design (CAD) software, and gear design expertise are often employed to overcome these challenges.
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material for gear manufacturing is crucial. Gears need to withstand high loads, transmit power efficiently, and exhibit excellent wear resistance. Selecting materials with suitable hardness, strength, and fatigue resistance can be challenging, especially when considering factors such as cost, availability, and compatibility with other components in the gear system.
- Manufacturing Processes: The manufacturing processes for producing spur gears, such as hobbing, shaping, or broaching, can present challenges. Achieving precise gear tooth profiles, accurate dimensions, and proper surface finish requires advanced machining techniques, specialized equipment, and skilled operators. Maintaining tight tolerances and ensuring consistent quality during mass production can also be demanding.
- Tooth Surface Finish: The surface finish of gear teeth plays a crucial role in gear performance. Achieving a smooth and precise tooth surface finish is challenging due to factors such as tool wear, heat generation during manufacturing, and the complexity of the gear tooth profile. Surface finishing processes, such as grinding or honing, may be required to achieve the desired surface quality.
- Noise and Vibration: Gears can generate noise and vibration during operation, which can affect the overall performance and user experience. Designing gears to minimize noise and vibration requires careful consideration of factors such as tooth profile optimization, load distribution, gear meshing characteristics, and proper lubrication. Conducting noise and vibration analysis and implementing appropriate design modifications may be necessary to address these challenges.
- Backlash Control: Controlling backlash, the slight gap between mating gear teeth, can be challenging. Backlash affects gear accuracy, smoothness of operation, and the ability to transmit torque efficiently. Balancing the need for adequate backlash to accommodate thermal expansion and minimize gear engagement issues while ensuring precise control of backlash can be a complex task in gear design and manufacturing.
- Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes, such as carburizing or quenching, are often employed to enhance the hardness and strength of gear teeth. Proper heat treatment is crucial to achieve the desired material properties and gear performance. However, challenges such as distortion, residual stresses, and material property variations can arise during heat treatment, requiring careful process control, post-heat treatment machining, or additional treatments to mitigate these challenges.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality and reliability of spur gears is a challenge in manufacturing. Implementing effective quality control measures, such as dimensional inspections, hardness testing, and gear tooth profile analysis, is essential. Statistical process control (SPC) techniques and quality assurance systems help monitor manufacturing processes, identify potential issues, and maintain consistent gear quality.
- Cost and Time Constraints: Designing and manufacturing spur gears that meet performance requirements within cost and time constraints can be challenging. Balancing factors such as material costs, tooling expenses, production lead times, and market competitiveness requires careful consideration and optimization. Efficient production planning, cost analysis, and value engineering techniques are often employed to address these challenges.
By recognizing these challenges and employing appropriate design methodologies, manufacturing techniques, and quality control measures, it is possible to overcome the potential challenges associated with designing and manufacturing spur gears.
It’s important to note that the specific challenges may vary depending on the gear application, size, complexity, and operating conditions. Collaboration with gear design experts, manufacturing engineers, and industry specialists can provide valuable insights and guidance in addressing the challenges specific to your spur gear design and manufacturing processes.

What is the lifespan of a typical spur gear?
The lifespan of a typical spur gear can vary significantly depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
The lifespan of a spur gear is influenced by various factors, including:
- Operating Conditions: The conditions under which the spur gear operates greatly impact its lifespan. Factors such as the magnitude and frequency of the applied loads, operating temperature, speed, and lubrication quality play a significant role. Gears operating under heavy loads, high speeds, or harsh environments may experience higher wear and fatigue, potentially reducing their lifespan.
- Material Selection: The material used for constructing the spur gear affects its durability and lifespan. Spur gears are commonly made from materials such as steel, cast iron, bronze, or polymer composites. The specific material properties, including hardness, strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion, influence the gear’s ability to withstand the operating conditions and determine its lifespan.
- Quality of Manufacturing: The quality of manufacturing processes and techniques employed during the production of the spur gear can impact its lifespan. Gears manufactured with precision, accurate tooth profiles, and proper heat treatment are more likely to have longer lifespans compared to those with manufacturing defects or poor quality control.
- Lubrication and Maintenance: Proper lubrication is crucial for reducing friction, wear, and heat generation in spur gears. Regular maintenance practices, including lubricant replacement, gear inspections, and addressing any issues promptly, can significantly extend the lifespan of the gears. Inadequate lubrication or neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear and failure.
- Load and Stress Distribution: The design and configuration of the gear system affect the load and stress distribution on the spur gears. Proper gear design, including tooth profile, number of teeth, and gear arrangement, helps ensure even load distribution and minimizes localized stress concentrations. Well-designed supporting components, such as bearings and shafts, also contribute to the overall lifespan of the gear system.
It is challenging to provide a specific lifespan for a typical spur gear since it depends on the aforementioned factors and the specific application. Spur gears can have lifespans ranging from several thousand to millions of operating cycles. Industrial gear systems often undergo regular inspections and maintenance, including gear replacement when necessary, to ensure safe and reliable operation.
It’s important to note that gear lifespan can be extended through proper care, maintenance, and adherence to recommended operating parameters. Regular inspections, monitoring of gear performance, and addressing any signs of wear or damage promptly can help maximize the lifespan of spur gears.
When assessing the lifespan of spur gears for a particular application, it is advisable to consult manufacturers, industry standards, and experts with expertise in gear design and maintenance for accurate estimations and recommendations.
Are there different sizes and configurations of spur gears available?
Yes, there are various sizes and configurations of spur gears available to suit different applications and requirements. Here’s a detailed explanation of the different options when it comes to sizes and configurations of spur gears:
Sizes: Spur gears come in a wide range of sizes to accommodate different torque and speed requirements. The size of a spur gear is typically specified by its pitch diameter, which is the diameter of the pitch circle. The pitch diameter determines the gear’s overall size and the spacing between the teeth. Spur gears can range from small gears used in precision instruments to large gears used in heavy machinery and industrial equipment.
Module: Module is a parameter used to specify the size and spacing of the teeth on a spur gear. It represents the ratio of the pitch diameter to the number of teeth. Different module sizes are available to accommodate various gear sizes and applications. Smaller module sizes are used for finer tooth profiles and higher precision, while larger module sizes are used for heavier loads and higher torque applications.
Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on a spur gear can vary depending on the specific application. Gears with a higher number of teeth provide smoother operation and distribute the load more evenly, whereas gears with fewer teeth are typically used for higher speeds and compact designs.
Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is an important parameter that determines the shape and engagement of the teeth. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees. The selection of the pressure angle depends on factors such as load capacity, efficiency, and specific design requirements.
Profile Shift: Profile shift is a design feature that allows modification of the tooth profile to optimize the gear’s performance. It involves shifting the tooth profile along the gear’s axis, which can affect factors such as backlash, contact ratio, and load distribution. Profile shift can be positive (when the tooth profile is shifted towards the center of the gear) or negative (when the tooth profile is shifted away from the center).
Hub Configuration: The hub refers to the central part of the gear where it is mounted onto a shaft. Spur gears can have different hub configurations depending on the specific application. Some gears have a simple cylindrical hub, while others may have keyways, set screws, or other features to ensure secure and precise mounting.
Material and Coatings: Spur gears are available in various materials to suit different operating conditions and requirements. Common materials include steel, cast iron, brass, and plastic. Additionally, gears can be coated or treated with surface treatments such as heat treatment or coatings to enhance their wear resistance, durability, and performance.
Mounting Orientation: Spur gears can be mounted in different orientations depending on the application and space constraints. They can be mounted parallel to each other on parallel shafts, or they can be mounted at right angles using additional components such as bevel gears or shafts with appropriate bearings.
In summary, there is a wide range of sizes and configurations available for spur gears, including different pitch diameters, module sizes, number of teeth, pressure angles, profile shifts, hub configurations, materials, coatings, and mounting orientations. The selection of the appropriate size and configuration depends on factors such as torque requirements, speed, load capacity, space constraints, and specific application needs.


editor by Dream 2024-05-06
China Professional Customizing Precision Spur Gears for Various Construction Machinery straight bevel gear
Product Description
1) According to the different strength and performance, we choose the steel with strong compression;
2) Using Germany professional software and our professional engineers to design products with more reasonable size and better performance; 3) We can customize our products according to the needs of our customers,Therefore, the optimal performance of the gear can be exerted under different working conditions;
4) Quality assurance in every step to ensure product quality is controllable.
Product Paramenters
|
DRIVEN GEAR |
NUMBER OF TEETH |
18 |
|
MODULE |
11.111 |
|
|
LENTH |
302 | |
|
OUTER DIAMETER |
ø210 |
|
|
DIRECTION OF SPIRAL |
L |
|
|
ACCURACY OF SPLINE |
M55*1.5-6h |
|
|
NUMBER OF SPLINE |
31 |
|
DRIVEN GEAR |
NUMBER OF TEETH |
27 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
OUTER DIAMETER |
ø3 square meter, with building area of 72,000 square meters. More than 500 employees work in our company. Certification & honors Packaging & Shipping Packaging Detail:standard package(carton ,wooden pallet).
Cooperative customers HangZhou CHINAMFG Gear Co., Ltd. adheres to the concept of “people-oriented, prosper with science and technology; create high-quality products, contribute to the society; turn friendship, and contribute sincerely”, and will strive to create world automotive axle spiral bevel gear products.
How do you calculate the efficiency of a spur gear?Calculating the efficiency of a spur gear involves considering the power losses that occur during gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation: In a gear system, power is transmitted from the driving gear (input) to the driven gear (output). However, due to various factors such as friction, misalignment, and deformation, some power is lost as heat and other forms of energy. The efficiency of a spur gear represents the ratio of the output power to the input power, taking into account these power losses. Formula for Calculating Gear Efficiency: The efficiency (η) of a spur gear can be calculated using the following formula: η = (Output Power / Input Power) × 100% Where: η is the efficiency of the gear system expressed as a percentage. Output Power is the power delivered by the driven gear (output) in the gear system. Input Power is the power supplied to the driving gear (input) in the gear system. Factors Affecting Gear Efficiency: The efficiency of a spur gear is influenced by several factors, including:
Interpreting Gear Efficiency: The calculated gear efficiency indicates the percentage of input power that is effectively transmitted to the output. For example, if a gear system has an efficiency of 90%, it means that 90% of the input power is converted into useful output power, while the remaining 10% is lost as various forms of power dissipation. It’s important to note that gear efficiency is not constant and can vary with operating conditions, lubrication quality, gear wear, and other factors. The calculated efficiency serves as an estimate and can be influenced by specific system characteristics and design choices. By considering the factors affecting gear efficiency and implementing proper design, lubrication, and maintenance practices, gear efficiency can be optimized to enhance overall gear system performance and minimize power losses.
What lubrication is required for spur gears?The lubrication requirements for spur gears are essential to ensure smooth operation, minimize wear, reduce friction, and dissipate heat. Here’s a detailed explanation of the lubrication needed for spur gears: Spur gears typically require lubricants that possess specific characteristics to provide effective lubrication. These lubricants should have the following properties:
The specific type and grade of lubricant needed for spur gears depend on the application, operating conditions, and gear material. Common lubricants used for spur gears include mineral oils, synthetic oils, and grease. Synthetic lubricants are often preferred for their superior performance in terms of viscosity stability, oxidation resistance, and temperature extremes. When applying lubrication to spur gears, ensure that the lubricant is evenly distributed across the gear teeth. Proper lubrication can be achieved through methods such as oil bath lubrication, oil mist lubrication, or oil application directly onto the gear teeth. The lubrication interval and quantity should be based on the gear system’s operating conditions and the lubricant manufacturer’s recommendations. Regular inspection and maintenance of the gear system are necessary to monitor the lubricant condition, replenish as needed, and ensure the gears remain properly lubricated throughout their service life. It is important to consult the gear manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations, as they may provide specific lubrication requirements and considerations for their gear products.
Can you explain the concept of straight-cut teeth in spur gears?The concept of straight-cut teeth is fundamental to understanding the design and operation of spur gears. Straight-cut teeth, also known as straight teeth or parallel teeth, refer to the shape and arrangement of the teeth on a spur gear. Here’s a detailed explanation of the concept of straight-cut teeth in spur gears: Spur gears have teeth that are cut straight and parallel to the gear axis. Each tooth has a uniform width and thickness, and the tooth profile is a straight line. The teeth are evenly spaced around the circumference of the gear, allowing them to mesh with other spur gears. The key characteristics and concepts related to straight-cut teeth in spur gears include:
In summary, straight-cut teeth in spur gears refer to the straight and parallel arrangement of the gear’s teeth. The teeth have a uniform profile with a constant width and thickness. Understanding the concept of straight-cut teeth is essential for designing and analyzing spur gears, considering factors such as tooth profile, pitch circle, pressure angle, meshing characteristics, and the trade-offs between simplicity, efficiency, and noise considerations.
China manufacturer Standard and Special Steel Spur Gear helical bevel gearProduct Description
Standard And Special Steel Spur Gear
1. Our products passed TS16949 ISO-9001: 2000 quality management system verification Technological process The essential advantage of P / M parts production process is that it has the final forming ability and high material utilization rate. Our team
How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with spur gears?Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears involves modifying or replacing certain components to incorporate spur gears into the system. Here’s a detailed explanation: 1. Evaluate the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to determine its design, function, and limitations. Identify the specific components that need to be retrofitted with spur gears and understand how the system operates. 2. Design Considerations: Based on the evaluation, consider the design considerations for integrating spur gears into the system. This includes factors such as gear size, tooth profile, gear material, gear ratio, and torque requirements. Determine the specific gear specifications that are compatible with the existing system. 3. Gear Selection: Select the appropriate spur gears that meet the required specifications. Consider factors such as gear quality, load capacity, noise level, efficiency, and compatibility with the existing system components. Choose gears from reputable manufacturers or consult with a gear specialist for guidance. 4. Gear Positioning and Alignment: Determine the optimal positioning and alignment of the spur gears within the existing system. This involves identifying the gear locations, shaft connections, and ensuring proper alignment with other components such as bearings and couplings. Accurate positioning and alignment are crucial for efficient gear operation and longevity. 5. Modification or Replacement: Based on the design considerations and gear selection, proceed with the necessary modifications or replacements. This may involve removing existing components, such as gears with different tooth profiles, and replacing them with the selected spur gears. Ensure proper installation and secure attachment of the new gears. 6. Lubrication and Maintenance: Implement appropriate lubrication practices for the newly retrofitted spur gears. Consult gear manufacturers’ recommendations for lubricant type, quantity, and maintenance intervals. Proper lubrication ensures smooth gear operation, reduces wear, and extends gear life. 7. Testing and Validation: After the retrofitting process, conduct thorough testing and validation of the modified system. Verify that the spur gears are functioning as intended, ensuring proper engagement, smooth operation, and adequate load handling. Address any issues or discrepancies discovered during testing. 8. Documentation and Training: Create documentation detailing the retrofitting process, including gear specifications, installation procedures, and maintenance requirements. This documentation serves as a reference for future maintenance and helps ensure consistent gear performance. Additionally, provide training to relevant personnel on the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the retrofitted system. Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears requires careful planning, proper gear selection, precise installation, and thorough testing. By following these steps and considering the specific requirements of the system, it is possible to successfully incorporate spur gears and enhance the performance and functionality of the mechanical system.
How do you install a spur gear system?Installing a spur gear system involves several steps to ensure proper alignment, engagement, and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to install a spur gear system:
It’s important to follow the specific installation instructions provided by the gear manufacturer to ensure proper installation and operation. Additionally, consult any applicable industry standards and guidelines for gear system installation. By carefully following these installation steps, you can ensure a well-aligned and properly functioning spur gear system in your machinery or equipment.
What are the applications of spur gears?Spur gears find a wide range of applications in various mechanical systems due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. These gears are commonly used in numerous industries and equipment. Here’s a detailed explanation of the applications of spur gears:
These are just a few examples of the broad range of applications where spur gears are utilized. Their simplicity, reliability, and ability to transmit power and motion efficiently make them a popular choice in various industries and equipment.
China factory Custom Sizes of Standard and Special Steel Spur Gears raw gearProduct Description
My advantages: /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How do you retrofit an existing mechanical system with spur gears?Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears involves modifying or replacing certain components to incorporate spur gears into the system. Here’s a detailed explanation: 1. Evaluate the Existing System: Begin by thoroughly evaluating the existing mechanical system to determine its design, function, and limitations. Identify the specific components that need to be retrofitted with spur gears and understand how the system operates. 2. Design Considerations: Based on the evaluation, consider the design considerations for integrating spur gears into the system. This includes factors such as gear size, tooth profile, gear material, gear ratio, and torque requirements. Determine the specific gear specifications that are compatible with the existing system. 3. Gear Selection: Select the appropriate spur gears that meet the required specifications. Consider factors such as gear quality, load capacity, noise level, efficiency, and compatibility with the existing system components. Choose gears from reputable manufacturers or consult with a gear specialist for guidance. 4. Gear Positioning and Alignment: Determine the optimal positioning and alignment of the spur gears within the existing system. This involves identifying the gear locations, shaft connections, and ensuring proper alignment with other components such as bearings and couplings. Accurate positioning and alignment are crucial for efficient gear operation and longevity. 5. Modification or Replacement: Based on the design considerations and gear selection, proceed with the necessary modifications or replacements. This may involve removing existing components, such as gears with different tooth profiles, and replacing them with the selected spur gears. Ensure proper installation and secure attachment of the new gears. 6. Lubrication and Maintenance: Implement appropriate lubrication practices for the newly retrofitted spur gears. Consult gear manufacturers’ recommendations for lubricant type, quantity, and maintenance intervals. Proper lubrication ensures smooth gear operation, reduces wear, and extends gear life. 7. Testing and Validation: After the retrofitting process, conduct thorough testing and validation of the modified system. Verify that the spur gears are functioning as intended, ensuring proper engagement, smooth operation, and adequate load handling. Address any issues or discrepancies discovered during testing. 8. Documentation and Training: Create documentation detailing the retrofitting process, including gear specifications, installation procedures, and maintenance requirements. This documentation serves as a reference for future maintenance and helps ensure consistent gear performance. Additionally, provide training to relevant personnel on the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the retrofitted system. Retrofitting an existing mechanical system with spur gears requires careful planning, proper gear selection, precise installation, and thorough testing. By following these steps and considering the specific requirements of the system, it is possible to successfully incorporate spur gears and enhance the performance and functionality of the mechanical system.
What is the lifespan of a typical spur gear?The lifespan of a typical spur gear can vary significantly depending on several factors. Here’s a detailed explanation: The lifespan of a spur gear is influenced by various factors, including:
It is challenging to provide a specific lifespan for a typical spur gear since it depends on the aforementioned factors and the specific application. Spur gears can have lifespans ranging from several thousand to millions of operating cycles. Industrial gear systems often undergo regular inspections and maintenance, including gear replacement when necessary, to ensure safe and reliable operation. It’s important to note that gear lifespan can be extended through proper care, maintenance, and adherence to recommended operating parameters. Regular inspections, monitoring of gear performance, and addressing any signs of wear or damage promptly can help maximize the lifespan of spur gears. When assessing the lifespan of spur gears for a particular application, it is advisable to consult manufacturers, industry standards, and experts with expertise in gear design and maintenance for accurate estimations and recommendations.
How do spur gears contribute to power transmission?Spur gears play a crucial role in power transmission due to their specific design and tooth engagement. Here’s a detailed explanation of how spur gears contribute to power transmission:
Overall, spur gears are essential in power transmission systems due to their direct tooth engagement, uniform load distribution, high efficiency, speed and torque conversion capabilities, directional control, compatibility with other components, and the ability to form complex gear trains. These characteristics make spur gears a versatile and widely used choice for transmitting power in various applications across industries.
|